SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
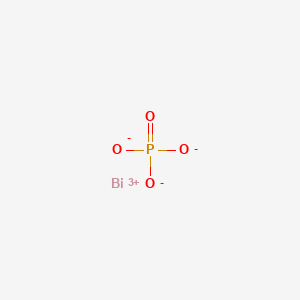
Product Name: Bismuth Phosphate
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. BI-PAT-02
, BI-PAT-03
, BI-PAT-04
, BI-PAT-05
CAS #: 10049-01-1
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Classification of the substance or mixture in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS)
The substance is not classified according to the Globally Harmonized System (GHS).
Hazards not otherwise classified: No data available
GHS label elements: N/A
Hazard pictograms: N/A
Signal word: N/A
Hazard statements: N/A
WHMIS classification: Not controlled
Classification system
HMIS ratings (scale 0-4)
(Hazardous Materials Identification System)
Health (acute effects) = 1
Flammability = 0
Physical Hazard = 0
Other hazards
Results of PBT and vPvB assessment
PBT: N/A
vPvB: N/A
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Substances
CAS No. / Substance Name:
10049-01-1 Bismuth(III) phosphate
Identification number(s):
EC number: 233-161-2
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Description of first aid measures
If inhaled:
Supply patient with fresh air. If not breathing, provide artificial respiration. Keep patient warm.
Seek immediate medical advice.
In case of skin contact:
Immediately wash with soap and water; rinse thoroughly.
Seek immediate medical advice.
In case of eye contact:
Rinse opened eye for several minutes under running water. Consult a physician.
If swallowed:
Seek medical treatment.
Information for doctor
Most important symptoms and effects, both acute and delayed
No data available
Indication of any immediate medical attention and special treatment needed
No data available
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing agents
Product is not flammable. Use fire-fighting measures that suit the surrounding fire.
Special hazards arising from the substance or mixture
If this product is involved in a fire, the following can be released:
Advice for firefighters
Protective equipment:
Wear self-contained respirator.
Wear fully protective impervious suit.
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Keep unprotected persons away.
Ensure adequate ventilation
Environmental precautions:
Do not allow material to be released to the environment without official permits.
Methods and materials for containment and cleanup:
Pick up mechanically.
Prevention of secondary hazards:
No special measures required.
Reference to other sections
See Section 7 for information on safe handling
See Section 8 for information on personal protection equipment.
See Section 13 for disposal information.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Handling
Precautions for safe handling
Keep container tightly sealed.
Store in cool, dry place in tightly closed containers.
Information about protection against explosions and fires:
The product is not flammable
Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Requirements to be met by storerooms and receptacles:
No special requirements.
Information about storage in one common storage facility:
Not required.
Further information about storage conditions:
Keep container tightly sealed.
Store in cool, dry conditions in well-sealed containers.
Specific end use(s)
No data available
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
Additional information about design of technical systems:
Properly operating chemical fume hood designed for hazardous chemicals and having an average face velocity of at least 100 feet per minute.
Control parameters
Components with limit values that require monitoring at the workplace: Not required.
Additional information: No data
Exposure controls
Personal protective equipment
Follow typical protective and hygienic practices for handling chemicals.
Keep away from foodstuffs, beverages and feed.
Remove all soiled and contaminated clothing immediately.
Wash hands before breaks and at the end of work.
Maintain an ergonomically appropriate working environment.
Breathing equipment:
Use suitable respirator when high concentrations are present.
Protection of hands: Impervious gloves
Inspect gloves prior to use.
Suitability of gloves should be determined both by material and quality, the latter of which may vary by manufacturer.
Penetration time of glove material (in minutes): No data available
Eye protection: Safety glasses
Body protection: Protective work clothing.
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Information on basic physical and chemical properties
Appearance:
Form: Powder
Color: White
Odor: Odorless
Odor threshold: No data available.
pH: N/A
Melting point/Melting range: Decomposes
Boiling point/Boiling range: No data available
Sublimation temperature / start: No data available
Flash point: N/A
Flammability (solid, gas): Product is not flammable.
Ignition temperature: No data available
Decomposition temperature: No data available
Autoignition: No data available.
Danger of explosion:
Product does not present an explosion hazard.
Explosion limits:
Lower: No data available
Upper: No data available
Vapor pressure: N/A
Density at 20 °C (68 °F): 6.32 g/cm3 (52.74 lbs/gal)
Relative density: No data available.
Vapor density: N/A
Evaporation rate: N/A
Solubility in Water (H2O): Insoluble
Partition coefficient (n-octanol/water): No data available.
Viscosity:
Dynamic: N/A
Kinematic: N/A
Other information
No data available
SECTION 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Reactivity
No data available
Chemical stability
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
Thermal decomposition / conditions to be avoided:
Decomposition will not occur if used and stored according to specifications.
Possibility of hazardous reactions
No dangerous reactions known
Conditions to avoid
No data available
Incompatible materials:
No data available
Hazardous decomposition products:
Phosphorus oxides (e.g. P2O5)
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Information on toxicological effects
Acute toxicity: No effects known.
LD/LC50 values that are relevant for classification: No data
Skin irritation or corrosion: May cause irritation
Eye irritation or corrosion: May cause irritation
Sensitization: No sensitizing effects known.
Germ cell mutagenicity: No effects known.
Carcinogenicity:
No classification data on carcinogenic properties of this material is available from the EPA, IARC, NTP, OSHA or ACGIH.
Reproductive toxicity: No effects known.
Specific target organ system toxicity - repeated exposure: No effects known.
Specific target organ system toxicity - single exposure: No effects known.
Aspiration hazard: No effects known.
Subacute to chronic toxicity:
Inorganic phosphorus compounds may cause irritation and hemorrhages in the stomach as well as liver and kidney damage. Bone structure may be attacked, especially the jaw and teeth.
Bismuth compounds are often poorly absorbed. However exposure may cause loss of appetite, headache, skin rash, exodermatitis, kidney injury and jaundice.
Repeated or prolonged exposure may cause a bismuth line or black spots on the gums, foul breath and salivation.
Exposure to bismuth may cause injury to the mouth, esophagus and stomach. Symptoms may include loss of appetite, headache, skin rash, kidney damage and jaundice.
Subacute to chronic toxicity: No effects known.
Additional toxicological information:
To the best of our knowledge the acute and chronic toxicity of this substance is not fully known.
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Toxicity
Aquatic toxicity:
No data available
Persistence and degradability
No data available
Bioaccumulative potential
No data available
Mobility in soil
No data available
Additional ecological information:
Do not allow material to be released to the environment without official permits.
Avoid transfer into the environment.
Results of PBT and vPvB assessment
PBT: N/A
vPvB: N/A
Other adverse effects
No data available
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Waste treatment methods
Recommendation
Consult official regulations to ensure proper disposal.
Uncleaned packagings:
Recommendation:
Disposal must be made according to official regulations.
SECTION 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
UN-Number
DOT, IMDG, IATA
None
UN proper shipping name
DOT, IMDG, IATA
None
Transport hazard class(es)
DOT, ADR, IMDG, IATA
Class
None
Packing group
DOT, IMDG, IATA
None
Environmental hazards:
N/A
Special precautions for user
N/A
Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL73/78 and the IBC Code
N/A
Transport/Additional information:
Not dangerous according to the above specifications.
DOT
Marine Pollutant (DOT):
No
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
Safety, health and environmental regulations/legislation specific for the substance or mixture
GHS label elements: N/A
Hazard pictograms: N/A
Signal word: N/A
Hazard statements: N/A
National regulations
All components of this product are listed in the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Toxic Substances Control Act Chemical substance Inventory.
All components of this product are listed on the Canadian Non-Domestic Substances List (NDSL).
SARA Section 313 (specific toxic chemical listings)
Substance is not listed.
California Proposition 65
Prop 65 - Chemicals known to cause cancer
Substance is not listed.
Prop 65 - Developmental toxicity
Substance is not listed.
Prop 65 - Developmental toxicity, female
Substance is not listed.
Prop 65 - Developmental toxicity, male
Substance is not listed.
Information about limitation of use:
For use only by technically qualified individuals.
Other regulations, limitations and prohibitive regulations
Substance of Very High Concern (SVHC) according to the REACH Regulations (EC) No. 1907/2006.
Substance is not listed.
The conditions of restrictions according to Article 67 and Annex XVII of the Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 (REACH) for the manufacturing, placing on the market and use must be observed.
Substance is not listed.
Annex XIV of the REACH Regulations (requiring Authorisation for use)
Substance is not listed.
Chemical safety assessment:
A Chemical Safety Assessment has not been carried out.
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.
 The bismuth atom has a radius of 156 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 207 pm. In its elemental form, bismuth is a silvery white brittle metal. Bismuth is the most diamagnetic of all metals and, with the exception of mercury, its thermal conductivity is lower than any other metal.
The bismuth atom has a radius of 156 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 207 pm. In its elemental form, bismuth is a silvery white brittle metal. Bismuth is the most diamagnetic of all metals and, with the exception of mercury, its thermal conductivity is lower than any other metal.  Bismuth has a high electrical resistance, and has the highest Hall Effect of any metal (i.e., greatest increase in electrical resistance when placed in a magnetic field). Bismuth is found in bismuthinite and bismite. It is also produced as a byproduct of lead, copper, tin, molybdenum and tungsten extraction. Bismuth was first discovered by Early Man. The name Bismuth originates from the German word 'wissmuth,' meaning white mass.
Bismuth has a high electrical resistance, and has the highest Hall Effect of any metal (i.e., greatest increase in electrical resistance when placed in a magnetic field). Bismuth is found in bismuthinite and bismite. It is also produced as a byproduct of lead, copper, tin, molybdenum and tungsten extraction. Bismuth was first discovered by Early Man. The name Bismuth originates from the German word 'wissmuth,' meaning white mass.
 See more Phosphorus products.
See more Phosphorus products.