SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
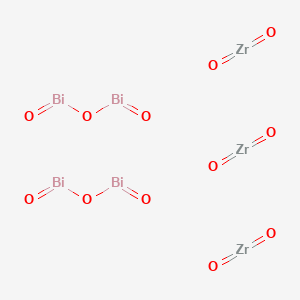
Product Name: Bismuth Zirconate
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. BI-ZRO-05-I
, BI-ZRO-05-L
, BI-ZRO-05-P
, BI-ZRO-05-ST
CAS #: 37306-42-6
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Physical hazards Not classified.
Health hazards Not classified.
Environmental hazards Not classified.
OSHA defined hazards Not classified.
Label elements
Hazard symbol None.
Signal word None.
Hazard statement The substance does not meet the criteria for classification.
Precautionary statement:
Prevention Observe good industrial hygiene practices.
Response Wash hands after handling.
Storage Store away from incompatible materials.
Disposal Dispose of waste and residues in accordance with local authority requirements.
Hazard(s) not otherwise classified (HNOC): None known.
Supplemental information None.
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Description: Magnesium Zirconate
CAS#: 37306-42-6
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Inhalation:
Move to fresh air. Call a physician if symptoms develop or persist.
Skin contact:
Wash off with soap and water. Get medical attention if irritation develops and persists.
Eye contact:
Rinse with water. Get medical attention if irritation develops and persists.
Ingestion:
Rinse mouth. Get medical attention if symptoms occur.
Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayed:
Direct contact with eyes may cause temporary irritation.
Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed:
Treat symptomatically.
General information:
Ensure that medical personnel are aware of the material(s) involved, and take precautions to
protect themselves.
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
Suitable extinguishing media:
Water fog. Foam. Dry chemical powder. Carbon dioxide (CO2).
Unsuitable extinguishing media:
Do not use water jet as an extinguisher, as this will spread the fire.
Specific hazards arising from the chemical:
During fire, gases hazardous to health may be formed.
Special protective equipment and precautions for firefighters:
Self-contained breathing apparatus and full protective clothing must be worn in case of fire.
Fire fighting equipment/instructions:
Move containers from fire area if you can do so without risk.
Specific methods:
Use standard firefighting procedures and consider the hazards of other involved materials.
General fire hazards:
No unusual fire or explosion hazards noted.
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures:
Keep unnecessary personnel away.
Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up:
Stop the flow of material, if this is without risk. Following product recovery, flush area with water.
Environmental precautions:
Avoid discharge into drains, water courses or onto the ground.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Precautions for safe handling:
Avoid prolonged exposure. Observe good industrial hygiene practices.
Conditions for safe storage including any incompatibilities:
Store in original tightly closed container.
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
Eye/face protection:
Wear safety glasses with side shields (or goggles).
Skin protection:
Wear appropriate chemical resistant gloves. Suitable gloves can be recommended by the glove
supplier.
Hand protection:
Other Wear suitable protective clothing.
Respiratory protection:
In case of insufficient ventilation, wear suitable respiratory equipment.
Thermal hazards:
Wear appropriate thermal protective clothing, when necessary.
General hygiene considerations:
Always observe good personal hygiene measures, such as washing after handling the material
and before eating, drinking, and/or smoking.
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Appearance
Physical state Solid.
Form Solid. Powder
Color Not available.
Odor Not available.
Odor threshold Not available.
pH Not available.
Melting point/freezing point Not available.
Initial boiling point and boiling range
Not available.
Flash point Not available.
Evaporation rate Not available.
Flammability (solid, gas) Not available.
Upper/lower flammability or explosive limits
Flammability limit - lower (%)
Not available.
Flammability limit - upper (%)
Not available.
Explosive limit - lower (%) Not available.
Explosive limit - upper (%) Not available.
Vapor pressure Not available.
Vapor density Not available.
Relative density Not available.
Solubility(ies)
Solubility (water) Not available.
Partition coefficient (n-octanol/water)
Not available.
Auto-ignition temperature Not available.
Decomposition temperature Not available.
Viscosity Not available.
Other information
Explosive properties Not explosive.
Molecular formula Bi4O12Zr3
Oxidizing properties Not oxidizing
SECTION 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Chemical stability Material is stable under normal conditions.
Possibility of hazardous:
No dangerous reaction known under conditions of normal use.
reactions
Conditions to avoid Contact with incompatible materials.
Incompatible materials:
Strong oxidizing agents.
Hazardous decomposition products:
No hazardous decomposition products are known.
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Information on likely routes of exposure
Inhalation Prolonged inhalation may be harmful.
Skin contact No adverse effects due to skin contact are expected.
Eye contact Direct contact with eyes may cause temporary irritation.
Ingestion Expected to be a low ingestion hazard.
Information on toxicological effects
Acute toxicity Not available.
Skin corrosion/irritation Prolonged skin contact may cause temporary irritation.
Serious eye damage/eye irritation Direct contact with eyes may cause temporary irritation.
Respiratory or skin sensitization
Respiratory sensitization Not a respiratory sensitizer.
Skin sensitization This product is not expected to cause skin sensitization.
Germ cell mutagenicity
No data available to indicate product or any components present at greater than 0.1% are
mutagenic or genotoxic
Carcinogenicity
Overall Evaluation of Carcinogenicity
Not listed.
OSHA Specifically Regulated Substances (29 CFR 1910.1001-1052)
Not regulated.
US. National Toxicology Program (NTP) Report on Carcinogens
Not listed.
Reproductive toxicity This product is not expected to cause reproductive or developmental effects.
Specific target organ toxicity -single exposure
Not classified.
Specific target organ toxicity -repeated exposure
Not classified.Aspiration hazard Not an aspiration hazard.
Chronic effects Prolonged inhalation may be harmful.
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Ecotoxicity The product is not classified as environmentally hazardous. However, this does not exclude the possibility that large or frequent spills can have a harmful or damaging effect on the environment.
Persistence and degradability No data is available on the degradability of this product.
Bioaccumulative potential No data available.
Mobility in soil No data available.
Other adverse effects No other adverse environmental effects (e.g. ozone depletion, photochemical ozone creation potential, endocrine disruption, global warming potential) are expected from this component.
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Disposal instructions
Collect and reclaim or dispose in sealed containers at licensed waste disposal site.
Local disposal regulations
Dispose in accordance with all applicable regulations.
Hazardous waste code
The waste code should be assigned in discussion between the user, the producer and the waste
disposal company.
Waste from residues / unused products
Dispose of in accordance with local regulations. Empty containers or liners may retain some
product residues. This material and its container must be disposed of in a safe manner (see:
Disposal instructions).
SECTION 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
DOT
Not regulated as dangerous goods.
IATA
Not regulated as dangerous goods.
IMDG
Not regulated as dangerous goods.
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
US federal regulations:
All components are on the U.S. EPA TSCA Inventory List.
This product is not known to be a "Hazardous Chemical" as defined by the OSHA Hazard
Communication Standard, 29 CFR 1910.1200.
Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA)
TSCA Section 12(b) Export Notification (40 CFR 707, Subpt. D)
Not regulated.
CERCLA Hazardous Substance List (40 CFR 302.4)
Not listed.
SARA 304 Emergency release notification
Not regulated.
OSHA Specifically Regulated Substances (29 CFR 1910.1001-1052)
Not regulated
Other federal regulations
Clean Air Act (CAA) Section 112 Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPs) List
Not regulated.
Clean Air Act (CAA) Section 112(r) Accidental Release Prevention (40 CFR 68.130)
Not regulated.
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.
 The bismuth atom has a radius of 156 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 207 pm. In its elemental form, bismuth is a silvery white brittle metal. Bismuth is the most diamagnetic of all metals and, with the exception of mercury, its thermal conductivity is lower than any other metal.
The bismuth atom has a radius of 156 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 207 pm. In its elemental form, bismuth is a silvery white brittle metal. Bismuth is the most diamagnetic of all metals and, with the exception of mercury, its thermal conductivity is lower than any other metal.  Bismuth has a high electrical resistance, and has the highest Hall Effect of any metal (i.e., greatest increase in electrical resistance when placed in a magnetic field). Bismuth is found in bismuthinite and bismite. It is also produced as a byproduct of lead, copper, tin, molybdenum and tungsten extraction. Bismuth was first discovered by Early Man. The name Bismuth originates from the German word 'wissmuth,' meaning white mass.
Bismuth has a high electrical resistance, and has the highest Hall Effect of any metal (i.e., greatest increase in electrical resistance when placed in a magnetic field). Bismuth is found in bismuthinite and bismite. It is also produced as a byproduct of lead, copper, tin, molybdenum and tungsten extraction. Bismuth was first discovered by Early Man. The name Bismuth originates from the German word 'wissmuth,' meaning white mass.
 The number of electrons in each of Zirconium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 10, 2 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d2 5s2. The zirconium atom has a radius of 160 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 186 pm. Zirconium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in 1789 and first isolated by Jöns Jakob Berzelius in 1824. In its elemental form, zirconium has a silvery white appearance that is similar to titanium. Zirconium's principal mineral is zircon (zirconium
The number of electrons in each of Zirconium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 10, 2 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d2 5s2. The zirconium atom has a radius of 160 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 186 pm. Zirconium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in 1789 and first isolated by Jöns Jakob Berzelius in 1824. In its elemental form, zirconium has a silvery white appearance that is similar to titanium. Zirconium's principal mineral is zircon (zirconium  Zirconium is commercially produced as a byproduct of
Zirconium is commercially produced as a byproduct of