SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
Product Name: Potassium Tetrafluoroaluminate
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. K-TFAL-02
, K-TFAL-03
, K-TFAL-04
, K-TFAL-05
CAS #: 14484-69-6
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Classification of the substance or mixture
GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS)
Acute toxicity, Oral(Category 3), H301
Skin corrosion(Category 1B), H314
Serious eye damage(Category 1), H318
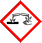
GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements
Pictogram

Signal word
Danger
Hazard statement(s)
H301
Toxic if swallowed.
H314
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
Precautionary statement(s)
P260
Do not breathe dust or mist.
P264
Wash skin thoroughly after handling.
P270
Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
P280
Wear protective gloves/ protective clothing/ eye protection/ face protection.
P301 + P310
IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor.
P301 + P
330 + P331
IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting.
P303 + P361 + P353
IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/ Take off immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse skin with water/ shower.
P304 + P340
IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
P305 + P351 + P338
IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
P310
Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor.
P321
Specific treatment (see supplemental first aid instructions on this label).
P363
Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P405
Store locked up.
P501
Dispose of contents/ container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Hazards not otherwise classified (HNOC) or not covered by GHS
Weak hydrogen fluoride-releaser
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
POTASSIUM TETRAFLUOROALUMINATE
14484-69-6
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
ORAL EXPOSURE
If swallowed, wash out mouth with water provided person is conscious. Call a physician.
INHALATION EXPOSURE
If inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give
oxygen.
DERMAL EXPOSURE
In case of contact, immediately wash skin with soap and copious amounts of water.
EYE EXPOSURE
In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water for at least 15
minutes.
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
FLASH POINT
N/A
AUTOIGNITION TEMP
N/A
FLAMMABILITY
N/A
EXTINGUISHING MEDIA
Suitable: Carbon dioxide, dry chemical powder, or appropriate foam.
FIREFIGHTING
Protective Equipment: Wear self-contained breathing apparatus and protective clothing to
prevent contact with skin and eyes.
Specific Hazard(s): Emits toxic fumes under fire conditions.
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
PROCEDURE(S) OF PERSONAL PRECAUTION(S)
Wear respirator, chemical safety goggles, rubber boots, and heavy rubber gloves.
METHODS FOR CLEANING UP
Sweep up, place in a bag and hold for waste disposal. Avoid raising dust. Ventilate area and wash spill site after material pickup is complete.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
HANDLING
User Exposure: Do not breathe dust. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothing. Avoid prolonged or repeated exposure.
STORAGE
Suitable: Keep tightly closed.
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
ENGINEERING CONTROLS
Safety shower and eye bath. Mechanical exhaust required.
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
Respiratory: Use respirators and components tested and approved under appropriate government
standards such as NIOSH (US) or CEN (EU). Where risk assessment shows air-purifying respirators are appropriate use a dust mask type N95 (US) or type P1 (EN 143) respirator.
Hand: Compatible chemical-resistant gloves.
Eye: Chemical safety goggles.
GENERAL HYGIENE MEASURES
Wash thoroughly after handling.
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Appearance
Physical State: Solid
Molecular Weight
142,0800 AMU
pH N/A
BP/BP Range N/A
MP/MP Range N/A
Freezing Point N/A
Vapor Pressure N/A
Vapor Density N/A
Saturated Vapor Conc. N/A
Bulk Density N/A
Odor Threshold N/A
Volatile% N/A
VOC Content N/A
Water Content N/A
Solvent Content N/A
Evaporation Rate N/A
Viscosity N/A
Surface Tension N/A
Partition Coefficient N/A
Decomposition Temp. N/A
Flash Point N/A
Explosion Limits N/A
Flammability N/A
Autoignition Temp N/A
Refractive Index N/A
Optical Rotation N/A
Miscellaneous Data N/A
Solubility N/A
SECTION 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
STABILITY
Stable: Stable.
Conditions to Avoid: Heat.
Materials to Avoid: Acids, Strong oxidizing agents.
HAZARDOUS DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS
Hazardous Decomposition Products: Hydrogen fluoride, Potassium oxides, Aluminum oxide.
HAZARDOUS POLYMERIZATION
Hazardous Polymerization: Will not occur
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE
Skin Contact: Causes skin irritation.
Skin Absorption: May be harmful if absorbed through the skin.
Eye Contact: Causes eye irritation.
Inhalation: Material is irritating to mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract. May be
harmful if inhaled.
Ingestion: May be harmful if swallowed.
TARGET ORGAN(S) OR SYSTEM(S)
Bones. Liver. Kidneys.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF EXPOSURE
Symptoms of exposure may include burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis,
shortness of breath, headache, nausea, and vomiting. Symptoms of fluoride overexposure may
include salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, and labored breathing. Fluoride ion can reduce serum calcium levels possibly causing fatal hypocalcemia.
Prolonged exposure to fluoride dusts, vapors, or mists results in perforation of the
nasal septum. Chronic effects include excessive calcification of the bones, ligaments, and
tendons.
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
No data available.
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
APPROPRIATE METHOD OF DISPOSAL OF SUBSTANCE OR PREPARATION
Contact a licensed professional waste disposal service to dispose of this material. Dissolve
or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped
with an afterburner and scrubber.
Observe all federal, state, and local environmental regulations.
SECTION 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
DOT (US)
UN number: 2923
Class: 8(6.1)
Packing group: IIl
Proper shipping name: Corrosive solids, toxic, n.o.s.(Potassium Tetrafluoroaluminate)
Poison Inhalation Hazard: No
IMDG
UN number: 2923
Class: 8(6.1)
Packing group: IIl
EMS-No: F-A, S-B
Proper shipping name: CORROSIVE SOLID, TOXIC, N.O.S.(Potassium Tetrafluoroaluminate)
IATA
UN number: 2923
Class: 8(6.1)
Packing group: IIl
Proper shipping name: Corrosive solid, toxic, n.o.s.(Potassium Tetrafluoroaluminate)
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
SARA 302 Components
No chemicals in this material are subject to the reporting requirements of SARA Title III, Section 302.
SARA 313 Components
This material does not contain any chemical components with known CAS numbers that exceed the threshold (De Minimis) reporting levels established by SARA Title III, Section 313.
SARA 311/312 Hazards
Acute Health Hazard, Chronic Health Hazard
Massachusetts Right To Know Components
No components are subject to the Massachusetts Right to Know Act.
Pennsylvania Right To Know Components
Potassium Tetrafluoroaluminate
CAS-No.
14484-69-6
Revision Date
2008-06-01
New Jersey Right To Know Components
Potassium Tetrafluoroaluminate
CAS-No.
14484-69-6
Revision Date
2008-06-01
California Prop. 65 Components
This product does not contain any chemicals known to State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or any other reproductive harm.
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.
 Aluminum's name is derived from alumina, the mineral from which Sir Humphrey Davy attempted to refine it from in 1812. Aluminum was first predicted by Antoine Lavoisier 1787 and first isolated by Hans Christian Øersted in 1825. Aluminum is a silvery gray metal that possesses many desirable characteristics. It is light, nonmagnetic and non-sparking. It stands second among metals in the scale of malleability, and sixth in ductility. It is extensively used in many industrial applications where a strong, light, easily constructed material is needed.
Aluminum's name is derived from alumina, the mineral from which Sir Humphrey Davy attempted to refine it from in 1812. Aluminum was first predicted by Antoine Lavoisier 1787 and first isolated by Hans Christian Øersted in 1825. Aluminum is a silvery gray metal that possesses many desirable characteristics. It is light, nonmagnetic and non-sparking. It stands second among metals in the scale of malleability, and sixth in ductility. It is extensively used in many industrial applications where a strong, light, easily constructed material is needed.  Although it has only 60% of the electrical conductivity of copper, it is used in electrical transmission lines because of its light weight. Pure aluminum is soft and lacks strength, but alloyed with small amounts of copper, magnesium, silicon, manganese, or other elements, it imparts a variety of useful properties.
Although it has only 60% of the electrical conductivity of copper, it is used in electrical transmission lines because of its light weight. Pure aluminum is soft and lacks strength, but alloyed with small amounts of copper, magnesium, silicon, manganese, or other elements, it imparts a variety of useful properties. See more Potassium products.
See more Potassium products. In its elemental form, potassium has a silvery gray metallic appearance, but its
In its elemental form, potassium has a silvery gray metallic appearance, but its