SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
Product Name: Rubidium Dihydrogenarsenate
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. RB-ASOH2-02
, RB-ASOH2-03
, RB-ASOH2-04
, RB-ASOH2-05
CAS #: 13464-57-8
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard Statements
Toxic if swallowed or if inhaled
May cause cancer
Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects
Precautionary Phrases
Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood
Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray.
Wash skin thoroughly after handling.
Do not eat, drink, or smoke when using this product.
Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
Avoid release into the environment
Use personal protective equipment as required.
IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed.
Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant.
HMIS CLASSIFICATION:
Health: 2 Fire: 0 Reactivity Hazard: 0
NFPA RATING:
Health: 2 Flammability: 0 Reactivity Hazard: 0
EYE CONTACT:
Risk of serious damage to eyes.
SKIN CONTACT:
Harmful if in contact with skin.
INHALATION:
Harmful by inhalation
INGESTION:
Toxic if swallowed.
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Formula:
RbH2AsO4
Molecular Weight:
226.40
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
EYE EXPOSURE:
In the case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
SKIN EXPOSURE:
Rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
INHALATION:
Remove to fresh air and keep at rest. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. Get medical attention if necessary.
INGESTION:
Do NOT induce vomiting. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. If conscious, wash out mouth with water. Get medical attention if necessary.
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
FLASH POINT:
Not available
AUTO IGNITION TEMPERATURE:
Not available
EXPLOSION LIMITS:
Not available
EXTINGUISHING MEDIUM:
Use dry chemical, carbon dioxide, water spray, or alcohol-resistant foam.
SPECIAL FIRE FIGHTING PROCEDURES:
Wear self-contained, approved breathing apparatus and full protective clothing,
including eye protection and boots.
HAZARDOUS COMBUSTION AND DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS:
Arsenic oxides and rubidium oxide
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
PERSONAL PRECAUTIONS:
Wear all appropriate equipment when using this material. Ensure adequate ventilation.
ENVIRONMENTAL PRECAUTIONS:
Prevent spillage from entering drains or allowing to be released into the environment.
METHODS AND MATERIALS FOR CONTAINMENT AND CLEANING UP:
Without creating dust, sweep up and shovel, and place in a suitable container for proper disposal.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
PRECAUTIONS FOR SAFE HANDLING:
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Use with adequate ventilation. Wash thoroughly after using. Keep container closed when not in use. Avoid formation of dusts and aerosols.
CONDITIONS FOR SAFE STORAGE:
Store in cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Keep away from oxidizing and spontaneously flammable products.
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
Exposure Controls
Component:
Rubidium dihydrogen arsenate
Exposure Limits:
0.01 mg/m3
Basis:
TLV
Entity:
ACGIH
EYE PROTECTION:
Wear chemical safety glasses or goggles and face shield
SKIN PROTECTION:
Wear nitrile or rubber gloves, and a complete suit protecting against chemicals
VENTILATION:
Provide local exhaust, preferably mechanical.
RESPIRATOR:
Use an approved respirator
ADDITIONAL PROTECTION:
Provide eyewash stations, quick-drench showers and washing facilities accessible to areas of use and handling.
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
COLOR AND FORM: White solid
ODOR: No data available
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 226.40
BOILING POINT: No data available
MELTING POINT: 268° C
SPECIFIC GRAVITY: No data available
VAPOR DENSITY: No data available
SOLUBILITY: Insoluble
SECTION 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
STABILITY: Stable
HAZARDOUS POLYMERIZATION: Will not occur
CONDITIONS TO AVOID: Exposure to air or moisture over prolonged periods
INCOMPATIBILITY: Strong oxidizing agents and metals.
DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS: Arsenic oxides and rubidium oxide
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
ACUTE TOXICITY: Not available
CARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: This product is a known carcinogen to humans according to IARC and NTP.
MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available
TETRATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
May cause long-term effects in aquatic environment.
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Dispose of in according to local, state, and federal regulations
SECTION 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
DOT: UN1557
Arsenic compounds, solid, n.o.s.
(Rubidium dihydrogen arsenate)
CLASS 6.1
PG II
IATA: UN1557
Arsenic compounds, solid, n.o.s.
(Rubidium dihydrogen arsenate)
CLASS 6.1
PG II
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
TSCA: Listed in the TSCA inventory
DSCL (EEC): Listed on the DSCL inventory
SARA 302/304: Not Listed
SARA 311/312: Acute Health Hazard, Chronic Health Hazard
SARA (TITLE 313): Rubidium dihydrogen arsenate
CALIFORNIA PROP. 65: Rubidium dihydrogen arsenate
MASSACHUSETTS RIGHT TO KNOW COMPONENTS: Rubidium dihydrogen arsenate
NEW JERSEY RIGHT TO KNOW COMPONENTS: Rubidium dihydrogen arsenate
PENNSYLVANIA RIGHT TO KNOW COMPONENTS: Rubidium dihydrogen arsenate"
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.
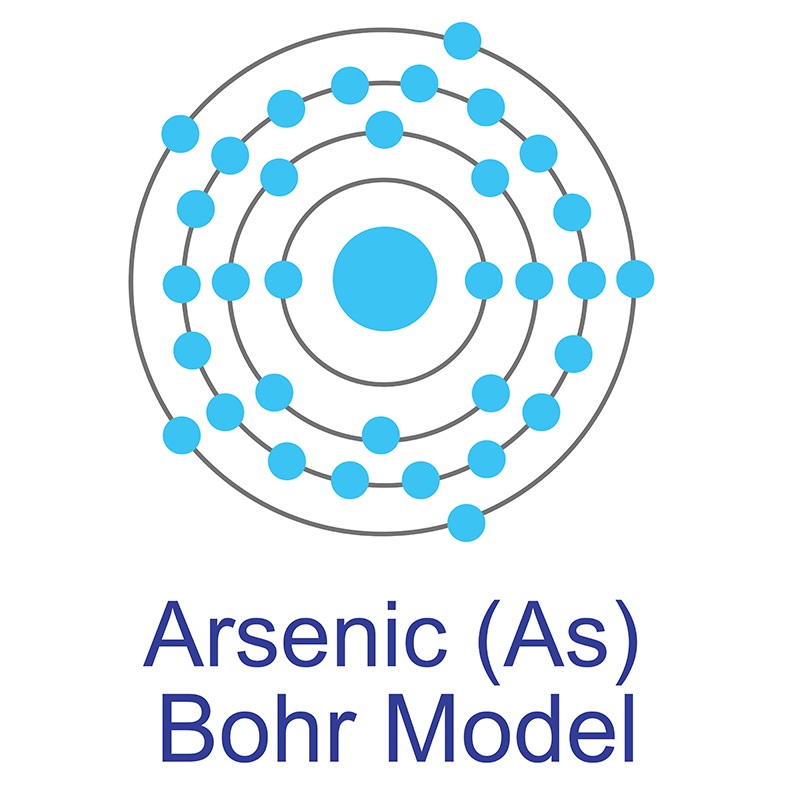 The number of electrons in each of arsenic's shells is 2, 8, 18, 5 and its electron configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3. The arsenic atom has a radius of 119 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 185 pm. Arsenic was discovered in the early Bronze Age, circa 2500 BC. It was first isolated by Albertus Magnus in 1250 AD. In its elemental form, arsenic is a metallic grey, brittle, crystalline, semimetallic solid.
The number of electrons in each of arsenic's shells is 2, 8, 18, 5 and its electron configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3. The arsenic atom has a radius of 119 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 185 pm. Arsenic was discovered in the early Bronze Age, circa 2500 BC. It was first isolated by Albertus Magnus in 1250 AD. In its elemental form, arsenic is a metallic grey, brittle, crystalline, semimetallic solid.  Arsenic is found in numerous minerals including arsenolite (As2O3), arsenopyrite (FeAsS), loellingite (FeAs2), orpiment (As2S3), and realgar (As4S4). Arsenic has numerous applications as a
Arsenic is found in numerous minerals including arsenolite (As2O3), arsenopyrite (FeAsS), loellingite (FeAs2), orpiment (As2S3), and realgar (As4S4). Arsenic has numerous applications as a  Rubidium is highly reactive, with properties similar to other Group 1 alkali
Rubidium is highly reactive, with properties similar to other Group 1 alkali