SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
Product Name: Silica Gel
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. SI-OX-01-GL
CAS #: 112926-00-8
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
This chemical is considered hazardous by the 2012 OSHA Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200).
Classification
Respiratory sensitization Category 1
Skin sensitization Category 1
Carcinogenicity Category 2
Reproductive toxicity Category 1B
Label elements
Signal word Danger
Hazard statements
May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if
inhaled
May cause an allergic skin reaction
Suspected of causing cancer
May damage fertility or the unborn child

Symbols/Pictograms
Precautionary Statements - Prevention Obtain special instructions before use
Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and
understood
Use personal protective equipment as required
Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray
In case of inadequate ventilation wear respiratory protection
Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the
workplace
Wear protective gloves
Precautionary Statements - Response
IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention
IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water
If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention
Wash contaminated clothing before reuse
IF INHALED: If breathing is difficult, remove victim to fresh air
and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing
If experiencing respiratory symptoms: Call a POISON CENTER
or doctor/physician
Precautionary Statements - Storage Store locked up
Precautionary Statements - Disposal Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal
plant
Hazards not otherwise classified (HNOC)
Hazards not otherwise classified (HNOC) N/A
Other Information
Unknown acute toxicity 100% of the mixture consists of ingredient(s) of unknown toxicity.
NFPA
Health: 0
Flammability: 0
Stability: 0
Physical and chemical -
properties
HMIS
Health: 0
Flammability: 0
Physical hazrds: 0
Personal protection -
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
CAS No 112926-00-8
Molecular Weight 60.08
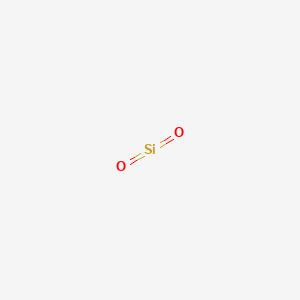
Formula O2Si
Chemical Name CAS No Weight % Oral LD50 Dermal LD50 Inhalation LC50
Silica gel 112926-00-8 >98 - - -
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
First Aid Measures
General advice Consult a physician if necessary. Remove to fresh air.
Eye contact Wash with plenty of water.
Skin Contact Wash skin with soap and water.
Inhalation Remove to fresh air If breathing is difficult, give oxygen If not breathing, give artificial
respiration
Ingestion Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Clean mouth with water.
Most important symptoms and effects, both acute and delayed
Symptoms No data available.
Indication of any immediate medical attention and special treatment needed
Note to physicians Treat symptomatically.
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
Suitable Extinguishing Media
Suitable Extinguishing Media Use extinguishing measures that are appropriate to local circumstances and the
surrounding environment.
Unsuitable Extinguishing Media None.
Specific hazards arising from the chemical
Specific hazards arising from the
chemical
No data available.
Hazardous combustion products No data available.
Explosion data
Sensitivity to Mechanical Impact No data available.
Sensitivity to Static Discharge No data available.
Protective equipment and precautions for firefighters
Protective equipment and precautions
for firefighters
As in any fire, wear self-contained breathing apparatus pressure-demand, MSHA/NIOSH
(approved or equivalent) and full protective gear.
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Personal precautions Ensure adequate ventilation, especially in confined areas.
Environmental precautions
Environmental precautions See Section 12 for additional Ecological Information.
Methods and material for containment and cleaning up
Methods for containment Prevent further leakage or spillage if safe to do so.
Methods for cleaning up Use personal protective equipment as required. Cover powder spill with plastic sheet or tarp
to minimize spreading and keep powder dry. Take up mechanically, placing in appropriate
containers for disposal. Avoid creating dust. Clean contaminated surface thoroughly.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Precautions for safe handling
Advice on safe handling Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice.
Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities Conditions Protect from moisture. Store at room temperature.
Incompatible materials None known based on information supplied
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
Control parameters
Exposure Guidelines .
Other Information Vacated limits revoked by the Court of Appeals decision in AFL-CIO v. OSHA, 965 F.2d 962
(11th Cir., 1992).
Chemical Name ACGIH TLV OSHA PEL NIOSH IDLH
Silica gel
112926-00-8
- (vacated) TWA: 6 mg/m3
TWA: 20 mppcf
: (80)/(% SiO2) mg/m3 TWA
-
Appropriate engineering controls
Engineering Controls Showers
Eyewash stations
Ventilation systems
Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment
Eye/face protection Wear safety glasses with side shields (or goggles).
Skin and Body Protection Wear protective gloves and protective clothing.
Respiratory protection If exposure limits are exceeded or irritation is experienced, NIOSH/MSHA approved
respiratory protection should be worn. Positive-pressure supplied air respirators may be
required for high airborne contaminant concentrations. Respiratory protection must be
provided in accordance with current local regulations.
General Hygiene Considerations Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice.
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Physical State Solid
Appearance powder or granules
Odor Odorless
Property
Values
pH No data available
Melting point/freezing point 1710 °C
Boiling point 2230 °C
Flash point No data available
Density No data available
Evaporation rate No data available
Upper flammability limits No data available
Lower flammability limit No data available
Vapor pressure No data available
Vapor density No data available
Specific gravity No data available
Water solubility No data available
Solubility in other solvents No data available
Partition coefficient No data available
Autoignition temperature No data available
Decomposition temperature No data available
Kinematic viscosity No data available
Explosive properties No data available
Oxidizing properties No data available
SECTION 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Reactivity N/A
Chemical stability Stable under recommended storage conditions.
Possibility of Hazardous Reactions None under normal processing.
Hazardous polymerization No data available.
Conditions to avoid Exposure to air or moisture over prolonged periods.
Incompatible materials Strong oxidizing agents.
Hazardous Decomposition Products None known based on information supplied
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Information on likely routes of exposure
Inhalation No data available.
Eye contact No data available.
Skin Contact No data available.
Ingestion No data available.
Information on toxicological effects
Symptoms No data available.
Delayed and immediate effects as well as chronic effects from short and long-term exposure
Chronic Toxicity No data available.
Carcinogenicity The table below indicates whether each agency has listed any ingredient as a carcinogen.
Chemical Name ACGIH IARC NTP OSHA
Silica gel
112926-00-8
- Group 3 - -
IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer) Not classifiable as a human carcinogen
Numerical measures of toxicity - Product Information
Unknown acute toxicity 100% of the mixture consists of ingredient(s) of unknown toxicity
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Ecotoxicity May cause long lasting harmful effects to aquatic life
0% of the mixture consists of components(s) of unknown hazards to the aquatic environment.
Persistence and degradability No data available.
Bioaccumulation No data available.
Mobility No data available.
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Disposal of wastes Disposal should be in accordance with applicable regional, national and local laws and
regulations.
Contaminated packaging Do not reuse container.
SECTION 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
DOT Not regulated
IMDG Not regulated
IATA Not regulated
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
International Inventories
All of the components in the product are on the following Inventory lists
Canada (DSL/NDSL) Australia (AICS) South Korea (KECL): China (IECSC) ENCS (Japan): Philippines (PICCS)
Chemical Name TSCA DSL NDSL EINECS ELINCS ENCS IECSC KECL PICCS AICS
Silica gel - X - - - X X X X X
X - Listed
TSCA - United States Toxic Substances Control Act Section 8(b) Inventory
DSL/NDSL - Canadian Domestic Substances List/Non-Domestic Substances List
EINECS/ELINCS - European Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances/European List of Notified Chemical Substances
ENCS - Japan Existing and New Chemical Substances
IECSC - China Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances
KECL - Korean Existing and Evaluated Chemical Substances
PICCS - Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances
US Federal Regulations
SARA 313
Section 313 of Title III of the Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986 (SARA). This product does not contain any
chemicals which are subject to the reporting requirements of the Act and Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 372.
SARA 311/312 Hazard Categories
Acute health hazard No
Chronic Health Hazard No
Fire hazard No
Sudden release of pressure hazard No
Reactive hazard No
CWA (Clean Water Act)
This product does not contain any substances regulated as pollutants pursuant to the Clean Water Act (40 CFR 122.21 and 40
CFR 122.42).
US State Regulations
California Proposition 65
This product does not contain any Proposition 65 chemicals.
U.S. State Right-to-Know Regulations
Chemical Name New Jersey Massachusetts Pennsylvania
Silica gel
112926-00-8
X X X
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.
![]() The number of electrons in each of Silicon's shells is 2, 8, 4 and its electron configuration is [Ne] 3s2 3p2. The silicon atom has a radius of 111 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 210 pm. Silicon was discovered and first isolated by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1823. Silicon makes up 25.7% of the earth's crust, by weight, and is the second most abundant element, exceeded only by oxygen. The metalloid is rarely found in pure crystal form and is usually produced from the iron-silicon alloy ferrosilicon.
The number of electrons in each of Silicon's shells is 2, 8, 4 and its electron configuration is [Ne] 3s2 3p2. The silicon atom has a radius of 111 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 210 pm. Silicon was discovered and first isolated by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1823. Silicon makes up 25.7% of the earth's crust, by weight, and is the second most abundant element, exceeded only by oxygen. The metalloid is rarely found in pure crystal form and is usually produced from the iron-silicon alloy ferrosilicon. ![]() Silica (or silicon dioxide), as sand, is a principal ingredient of glass, one of the most inexpensive of materials with excellent mechanical, optical, thermal, and electrical properties. Ultra high purity silicon can be doped with boron, gallium, phosphorus, or arsenic to produce silicon for use in transistors, solar cells, rectifiers, and other solid-state devices which are used extensively in the electronics industry.The name Silicon originates from the Latin word silex which means flint or hard stone.
Silica (or silicon dioxide), as sand, is a principal ingredient of glass, one of the most inexpensive of materials with excellent mechanical, optical, thermal, and electrical properties. Ultra high purity silicon can be doped with boron, gallium, phosphorus, or arsenic to produce silicon for use in transistors, solar cells, rectifiers, and other solid-state devices which are used extensively in the electronics industry.The name Silicon originates from the Latin word silex which means flint or hard stone.