About Lawrencium
Lawrencium, the last element of the actinide series, was first synthesized at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in 1961 by the nuclear-physics team headed by Albert Ghiorso. The synthesis was achieved by bombarding a californium target with boron-10 and boron-11 from the heavy ion linear accelerator. This team was responsible for the element being named in honor of Ernest O. Lawrence, who built the first working cyclotron. However, the initial experiments by the Berkeley team did not produce all the data ideally desired to prove an element's existence--this data came from later Berkeley experiments as well as from work by the Russian Joint Institute for Nuclear Research. IUPAC officially recognized both teams as co-discoverers of the element in 1992.
Because only a few atoms have ever been created, and the isotopes have very short half-lives, scientists have not had sufficient opportunity to study the element in detail. Consequently, it has no commercial applications and little is known about its characteristics.
Lawrencium Properties
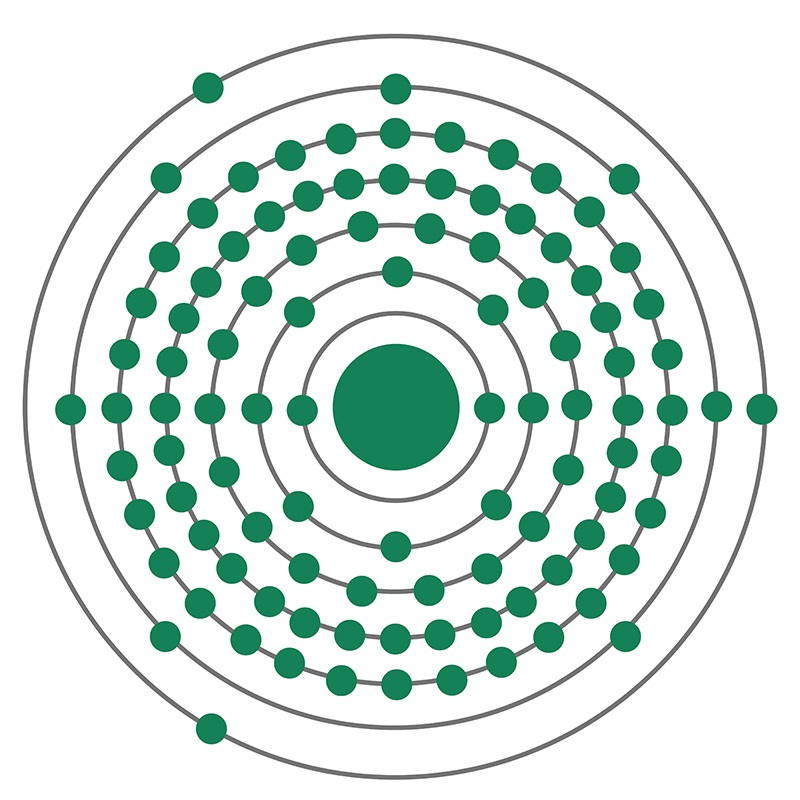
 Lawrencium is a Block D, Group 3, Period 7 element. The number of electrons in each of lawrencium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 8, 3, and its electron configuration is [Rn] 5f147s27p. The lawrencium atom has a Van der Waals radius of 246.pm. In its elemental form, lawrencium's CAS number is 22537-19-5. Lawrencium behaves differently from dipositive nobelium and more like the tripositive elements found earlier in the actinide series. Lawrencium is radioactive and therefore considered toxic. Lawrencium was discovered by Albert Ghiorso, Torbjorn Sikkeland, Almon E. Larsh and Robert M. Latimer at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in 1961. It was named after Earnest O. Lawrence the inventor of the cyclotron particle accelerator. The symbol for Lawrencium was originally Lw; however, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) changed the symbol from Lw to Lr in August, 1997.
Lawrencium is a Block D, Group 3, Period 7 element. The number of electrons in each of lawrencium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 8, 3, and its electron configuration is [Rn] 5f147s27p. The lawrencium atom has a Van der Waals radius of 246.pm. In its elemental form, lawrencium's CAS number is 22537-19-5. Lawrencium behaves differently from dipositive nobelium and more like the tripositive elements found earlier in the actinide series. Lawrencium is radioactive and therefore considered toxic. Lawrencium was discovered by Albert Ghiorso, Torbjorn Sikkeland, Almon E. Larsh and Robert M. Latimer at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in 1961. It was named after Earnest O. Lawrence the inventor of the cyclotron particle accelerator. The symbol for Lawrencium was originally Lw; however, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) changed the symbol from Lw to Lr in August, 1997.
Lawrencium information, including technical data, properties, and other useful facts are discussed below. Scientific facts such as the atomic structure, ionization energy, abundance on Earth, conductivity and thermal properties are included.
Lawrencium Isotopes
Lawrencium is an artificial element. It has no stable isotopes.
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 252Lr | 252.09526(26)# | 390(90) ms [0.36(+11-7) s] | a to 248Md; EC to 252No; SF | N/A | N/A | 1872.72998 | - |
| 253Lr | 253.09509(22)# | 580(70) ms [0.57(+7-6) s] | a to 249Md; EC to 253No; SF | (7/2-) | N/A | 1887.464966 | - |
| 254Lr | 254.09648(32)# | 13(3) s | a to 250Md; EC to 254No; SF | N/A | N/A | 1879.562988 | - |
| 255Lr | 255.096562(19) | 22(4) s | a to 251Md; EC to 255No | 7/2-# | N/A | 1887.464966 | - |
| 256Lr | 256.09849(9) | 27(3) s | a to 252Md; EC to 256No; SF | N/A | N/A | 1893.678955 | - |
| 257Lr | 256.09849(9) | 646(25) ms | a to 253Md | 9/2+# | N/A | 1900.964966 | - |
| 258Lr | 258.10176(11)# | 3.9 s | a to 254Md; EC to 258No; SF | N/A | N/A | 1906.916016 | - |
| 259Lr | 259.10290(8)# | 6.1 s | a to 255Md; EC to 259No; SF | 9/2+# | N/A | 1913.954956 | - |
| 260Lr | 260.10551(13)# | 4.1(3) s | a to 256Md; EC to 260No; SF | N/A | N/A | 1919.620972 | - |
| 261Lr | 261.10688(22)# | 40 m | SF | N/A | N/A | 1926.417969 | - |
| 262Lr | 262.10961(22)# | 3.6 h | EC to 262No; SF | N/A | N/A | 1931.927002 | - |
| 263Lr | 263.11136(30)# | s# h; | a to 259Md | N/A | N/A | 1938.412964 | - |
| 264Lr | 264.11420(47)# | 10# h | a to 261Md | N/A | N/A | N/A | - |
| 265Lr | 265.11619(65)# | 10# h | a to 261Md | N/A | N/A | N/A | - |
| 266Lr | 266.11983(56)# | 11 h | SF | N/A | N/A | N/A | - |