About Mendelevium
Mendelevium, a radioactive transuranic actinide, was the first element to be synthesized one atom at a time and the ninth transuranic element to be synthesized. The painstaking task, completed by a team at the University of California Berkely in 1955, produced a total of only seventeen atoms. The synthesis required bombarding einsteinium-253, itself a synthetic element that requires significant effort to prepare and isolate in appreciable quantities, with alpha particles in the Berkeley lab's cyclotron. Following the synthesis, the seventeen atoms of the new element were purified using ion-exchange chromatography. The element's discovery, as well as its naming after the father of the modern periodic table, Dimitri Mendeleev, were accepted by the IUPAC later in 1955.
One of the superheavy elements, mendelevium is very unstable, with the most stable isotope having a half-life of about 55 days, and the originally synthesized isotope, mendelevium-56, having a half-life of only 87 minutes. Mendelevium has no commercial applications, but remains of interest to science researchers.
Mendelevium Properties
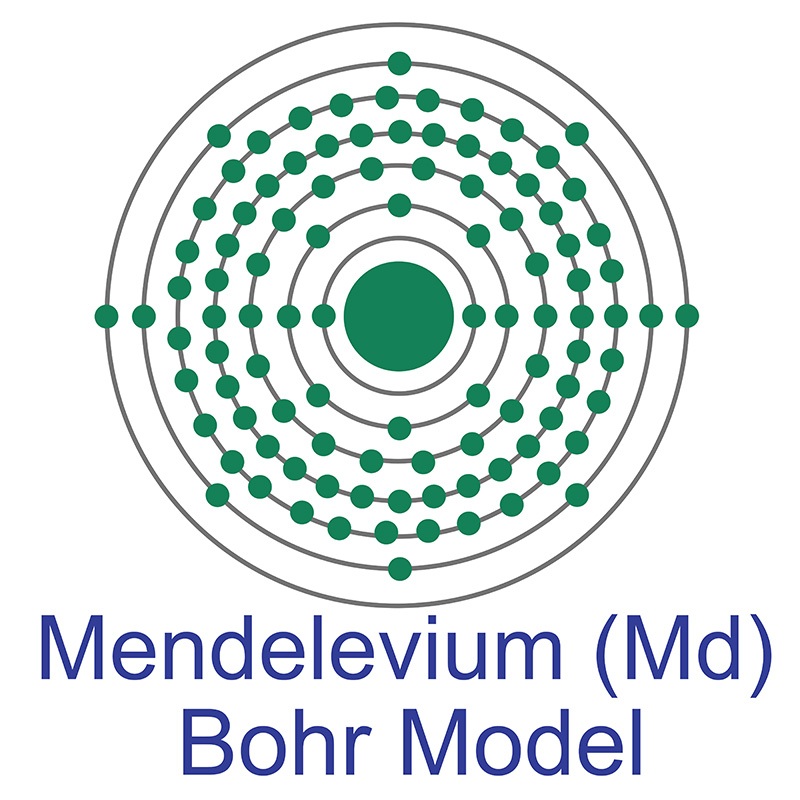 Mendelevium is a Block F, Group 3, Period 7 element. The number of electrons in each of mendelevium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 32, 31, 8, 2 and its electronic configuration is [Rn] 5f13 7s2. The mendelevium atom has a Van der Waals radius of 246.pm. In its elemental form, mendelevium's CAS number is 7440-11-1. Mendelevium is radioactive and therefore considered harmful. Mendelevium was discovered by Albert Ghiorso, Bernard G. Harvey, Gregory R. Choppin, Stanley G. Thompson and Glenn T. Seaborg at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in 1955. Mendelevium was named after Russian chemist Dmitri Ivanovitch Mendeleyev, who created the periodic table. Mendelevium is a synthetic element that is usually produced by bombarding einsteinium with alpha particles. Mendelevium was the ninth transuranic element of the actinide series to be discovered.
Mendelevium is a Block F, Group 3, Period 7 element. The number of electrons in each of mendelevium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 32, 31, 8, 2 and its electronic configuration is [Rn] 5f13 7s2. The mendelevium atom has a Van der Waals radius of 246.pm. In its elemental form, mendelevium's CAS number is 7440-11-1. Mendelevium is radioactive and therefore considered harmful. Mendelevium was discovered by Albert Ghiorso, Bernard G. Harvey, Gregory R. Choppin, Stanley G. Thompson and Glenn T. Seaborg at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in 1955. Mendelevium was named after Russian chemist Dmitri Ivanovitch Mendeleyev, who created the periodic table. Mendelevium is a synthetic element that is usually produced by bombarding einsteinium with alpha particles. Mendelevium was the ninth transuranic element of the actinide series to be discovered.
Mendelevium information, including technical data, properties, and other useful facts are discussed below. Scientific facts such as the atomic structure, ionization energy, abundance on Earth, conductivity and thermal properties are included.
Mendelevium Isotopes
Mendelevium is an artificial element. It has no stable isotopes.
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 245Md | 245.08081(33)# | 0.90(25) ms | SF | (1/2-)# | N/A | 1822.989014 | - |
| 246Md | 246.08171(28)# | 1.0(4) s | a to 242Es; ß+ to 246Fm | N/A | N/A | 1830.208008 | - |
| 247Md | 247.08152(22)# | 1.12(22) s | SF | 1/2-# | N/A | 1838.399048 | - |
| 248Md | 248.08282(26)# | 7(3) s | ß+ to 248Fm; a to 244Es; SF | N/A | N/A | 1845.44104 | - |
| 249Md | 249.08291(22)# | 24(4) s | a to 243Es; ß+ to 247Fm | (7/2-) | N/A | 1853.426025 | - |
| 250Md | 250.08442(32)# | 52(6) s | ß+ to 250Fm; a to 246Es; SF | N/A | N/A | 1860.113037 | - |
| 251Md | 251.084774(20) | 4.0(5) min | ß+ to 251Fm; a to 247Es | 7/2-# | N/A | 1867.782959 | - |
| 252Md | 252.08643(14)# | 2.3(8) min | ß+ to 252Fm; a to 248Es | N/A | N/A | 1874.26001 | - |
| 253Md | 253.08714(3)# | 12(8) min [6(+12-3) min] | ß+ to 253Fm; a to 249Es | 7/2-# | N/A | 1881.725952 | - |
| 254Md | 254.08959(11)# | 10(3) min | ß+ to 254Fm; a to 250Es | (0-) | N/A | 1887.52002 | - |
| 255Md | 255.091084(7) | 27(2) min | ß+ to 255Fm; a to 251Es; SF | (7/2-) | N/A | 1894.333618 | - |
| 256Md | 256.09389(13)# | 77(2) min | ß+ to 256Fm; a to 252Es | (1-) | N/A | 1899.631348 | - |
| 257Md | 257.0955424(29) | 5.52(5) h | a to 253Es; EC to 257Fm; SF | (7/2-) | N/A | 1906.322388 | - |
| 258Md | 258.098431(5) | 51.5(3) d | EC to 258Fm | (8-)# | N/A | 1911.70105 | - |
| 259Md | 259.10051(22)# | 1.60(6) h | a to 255Es; SF | 7/2-# | N/A | 1917.837036 | - |
| 260Md | 260.10365(34)# | 27.8(8) d | EC to 260Fm; a to 256Es; ß- to 260No | N/A | N/A | 1922.980957 | - |
| 261Md | 261.10583(62)# | 40# min | a to 257Es | 7/2-# | N/A | N/A | - |
| 262Md | 262.10910(45)# | 3# min | SF | N/A | N/A | N/A | - |