About Rutherfordium
Rutherfordium was produced in the 1960s in labs in California and the Soviet Union, and both claimed its discovery. Due to the competing claims, the IUPAC gave element 106 the temporary systemic name Unnilquadium (Unq); the proposed names by the Soviets and the Americans were respectively Kurchatovium (Ku) in honor of Igor Kurchatov, head of Soviet nuclear research, and Rutherfordium, in honor of Ernest Rutherford, who is known as the father of nuclear physics and modern atomic theory. In 1997 the dispute was resolved by assigning the name of Rutherfordium to element 106 and Dubnium to 105 in honor of the location of the Soviet Joint Institute of Nuclear Research.
Rutherfordium is a radioactive material with an extremely short half-life, and only small amounts have been produced. The chemical properties are not fully known, but based on its position on the periodic table as the first transactinide element, its basic properties are predicted to be similar to the other elements in period 4 such as zirconium and hafnium. It is predicted to be a solid at room temperature with a hexagonal close-packed crystal structure and a density of around 23 g/cm3.
Rutherfordium Properties
 Rutherfordium is a P-Block, Group 4, Period 7 element.
Rutherfordium is a P-Block, Group 4, Period 7 element. 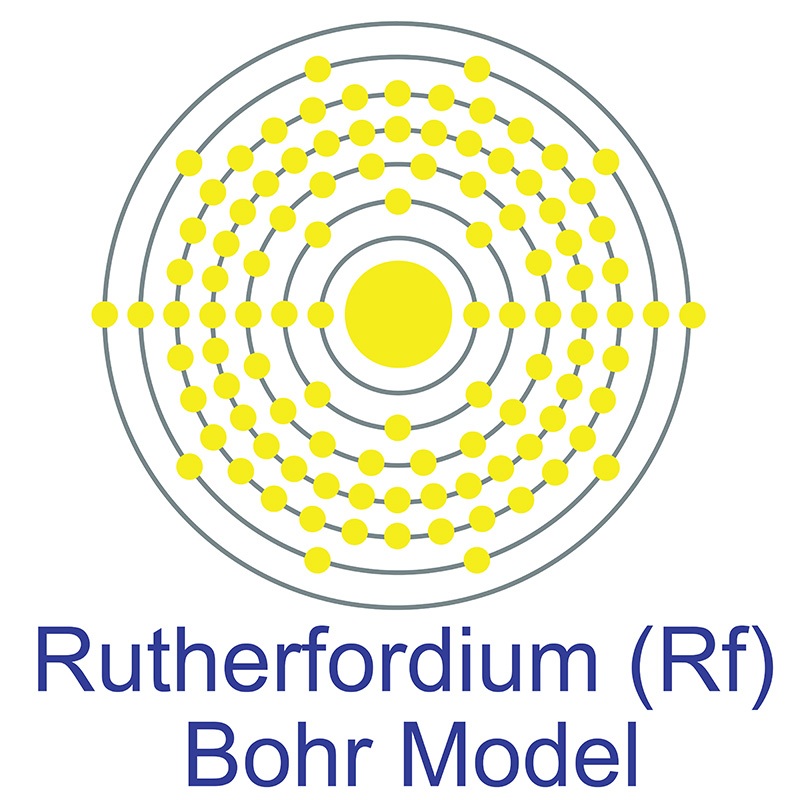 The number of electrons in each of Rutherfordium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 10, 2 and its electron configuration is [Rn] 5f14 6d2 7s2 . In its elemental form Rutherfordium's CAS number is 53850-36-5. Rutherfordium was first produced in 1964 at the Nuclear Institute at Dubna in the former Soviet Union and again in 1969 by an American group at the University of California, Berkeley. Rutherfordium is named in honor of the New Zealand physicist Ernest R. Rutherford .
The number of electrons in each of Rutherfordium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 10, 2 and its electron configuration is [Rn] 5f14 6d2 7s2 . In its elemental form Rutherfordium's CAS number is 53850-36-5. Rutherfordium was first produced in 1964 at the Nuclear Institute at Dubna in the former Soviet Union and again in 1969 by an American group at the University of California, Berkeley. Rutherfordium is named in honor of the New Zealand physicist Ernest R. Rutherford .
Rutherfordium Isotopes
Rutherfordium (Rf) is an artificial element. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes.
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 253Rf | 253.10044(44)# | 13(5) ms | SF; a to 249No | (7/2)(+#) | N/A | 1866.897949 | - |
| 254Rf | 254.10005(30)# | 23(3) µs | SF; a to 250No | 0+ | N/A | 1875.447021 | - |
| 255Rf | 255.10127(12)# | 1.64(11) s | a to 251No; SF | (9/2-)# | N/A | 1882.284058 | - |
| 256Rf | 256.101152(19) | 6.45(14) ms | a to 252No; SF | 0+ | N/A | 1890.645752 | - |
| 257Rf | 257.102918(12)# | 4.7(3) s | a to 253No; SF ; EC to 257Lr | (1/2+) | N/A | 1896.953979 | - |
| 258Rf | 258.10343(3) | 12(2) ms | a to 254No; SF | 0+ | N/A | 1904.562988 | - |
| 259Rf | 259.10560(8)# | 2.8(4) s | a to 255No; SF ; EC to 259Lr | 7/2+# | N/A | 1910.715942 | - |
| 260Rf | 260.10644(22)# | 21(1) ms | a to 256No; SF | 0+ | N/A | 1918.036987 | - |
| 261Rf | 261.10877(5) | 5.5(25) s | a to 257No; SF ; EC to 261Lr | 3/2+# | N/A | 1923.948975 | - |
| 262Rf | 262.10993(24)# | 2.3(4) s | SF | 0+ | N/A | 1930.93396 | - |
| 263Rf | 263.1125(2)# | 11(3) min | a to 259No; SF | 3/2+# | N/A | 1936.562988 | - |
| 264Rf | 264.11388(39)# | 1# h | SF | 0+ | N/A | 1943.295044 | - |
| 265Rf | 265.11668(39)# | 1.8 min | SF | N/A | N/A | N/A | - |
| 266Rf | 266.11817(50)# | 10# h | Unknown | 0+ | N/A | N/A | - |
| 267Rf | 267.12179(62)# | 5# h [2.3(+980-17) h] | SF | N/A | N/A | N/A | - |
| 268Rf | 268.12397(77)# | 1# h | Unknown | 0+ | N/A | N/A | - |
