About Krypton
Krypton, atomic number 36, is one of the noble gases and is found in trace amounts (1 ppm) of the Earth’s atmosphere. The high cost of fractional distillation of liquefied air to isolate this element precludes widespread use in practical applications. When isolated, krypton is commercially used for high-speed photographic flash bulbs; and when mixed with other gases such as argon, is often present in fluorescent lamps. Krypton is mostly inert and few compounds containing krypton are known to exist. Krypton diflouride (KrF2) is one such compound – a volatile and colorless solid that can typically only be produced in amounts measured in grams.
When krypton is combined with fluorine, a host of industrial and scientific applications are made possible. Krypton fluoride lasers produce a deep-ultraviolet beam that is widely used in photolithography during the manufacturing process of semiconductor integrated circuits. Due to the short wavelength of its emitted light (λ = 248 nm), this type of laser is credited with significantly reducing piece-part spacing in microelectronic chips throughout the 1990s and 2000s. This increased the density of piece-parts on a microchip, transistors in a CPU for example, thereby increasing switching speed and lowering cost of manufacturing electronic devices. For these reasons, the krypton fluoride laser has been credited as one of the key contributors in maintaining Moore’s Law during this time frame.
Sir William Ramsay, chemist and recipient of the 1904 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his isolation of noble gases, along with Morris Travers, discovered krypton in 1898 by evaporating components of liquefied air. Six naturally occurring, stable isotopes of krypton have been discovered since. One such isotope, 81Kr, has been found useful in dating groundwater. 85Kr is a byproduct of uranium or plutonium fission and is itself radioactive with a half-life of 10.76 years. 86Kr, with the 605nm wavelength characteristic of its orange-red spectral line, was declared the official internationally-accepted definition of ‘meter’ as a unit of measure in 1960; replacing a metal bar, before being replaced itself in 1983 by the distance that light travels in a vacuum.
Krypton Properties
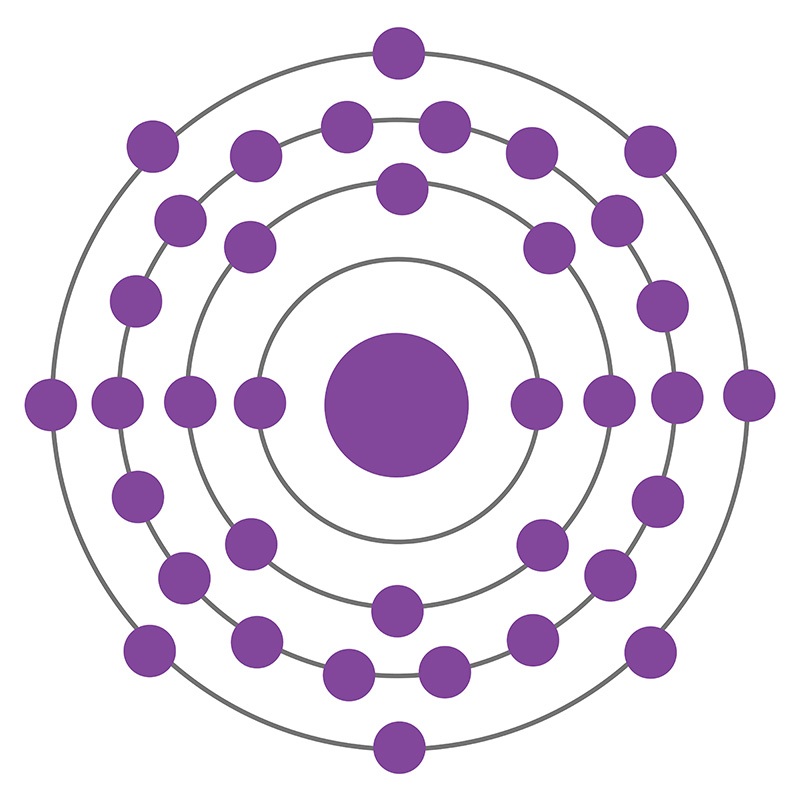
 Krypton is a Block P, Group 18, Period 4 element. The number of electrons in each of Krypton's shells is 2, 8, 18, 8 and its electronic configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p6. In its elemental form krypton's CAS number is 7439-90-9. The krypton atom has a covalent radius of 116±4.pm and it's Van der Waals radius is 202.pm. Krypton has a concentration about 1 ppm in the atmosphere and can be extracted from liquid air. Krypton was discovered and first isolated by Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers in 1898. The origin of the name Krypton comes from the Greek word kryptos meaning "hidden".
Krypton is a Block P, Group 18, Period 4 element. The number of electrons in each of Krypton's shells is 2, 8, 18, 8 and its electronic configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p6. In its elemental form krypton's CAS number is 7439-90-9. The krypton atom has a covalent radius of 116±4.pm and it's Van der Waals radius is 202.pm. Krypton has a concentration about 1 ppm in the atmosphere and can be extracted from liquid air. Krypton was discovered and first isolated by Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers in 1898. The origin of the name Krypton comes from the Greek word kryptos meaning "hidden".
Krypton information, including technical data, properties, and other useful facts are specified below. Scientific facts such as the atomic structure, ionization energy, abundance on Earth, conductivity, and thermal properties are included.
Health, Safety & Transportation Information for Krypton
Krypton is not toxic and is chemically inert, and thus poses minimal environmental or health threats. At room temperature, krypton is typically only harmful when its presence leads to displacement of oxygen in the air, creating potential for asphyxiation.
| Safety Data | |
|---|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet | MSDS |
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H280 |
| Hazard Codes | N/A |
| Risk Codes | N/A |
| Safety Precautions | N/A |
| RTECS Number | N/A |
| Transport Information | N/A |
| WGK Germany | nwg |
| Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling (GHS) |
|
Krypton Isotopes
Naturally occurring krypton has six stable isotopes: 78Kr, 80Kr, 82Kr, 83Kr, 84Kr, and 86Kr.
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69Kr | 68.96518(43)# | 32(10) ms | ß+ to 69Br | 5/2-# | N/A | 549.64 | - |
| 70Kr | 69.95526(41)# | 52(17) ms | ß+ to 70Br | 0+ | N/A | 567.04 | - |
| 71Kr | 70.94963(70) | 100(3) ms | ß+ to 71Br; ß+ + p to 70Se | (5/2)- | N/A | 580.71 | - |
| 72Kr | 71.942092(9) | 17.16(18) s | ß+ to 72Br | 0+ | N/A | 595.31 | - |
| 73Kr | 72.939289(7) | 28.6(6) s | ß+ to 73Br; ß+ + p to 72Se | 3/2- | N/A | 606.18 | - |
| 74Kr | 73.9330844(22) | 11.5 min | EC to 74Br | 0+ | N/A | 619.85 | - |
| 75Kr | 74.930946(9) | 4.3 min | EC to 75Br | 5/2+ | N/A | 630.72 | - |
| 76Kr | 75.925910(4) | 14.8 h | EC to 76Br | 0+ | N/A | 643.46 | - |
| 77Kr | 76.9246700(21) | 1.24 h | EC to 77Br | 5/2+ | N/A | 652.47 | - |
| 78Kr | 77.9203648(12) | Observationally Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 664.28 | 0.35 |
| 79Kr | 78.920082(4) | 1.455 d | EC to 79Br | 1/2- | N/A | 672.35 | - |
| 80Kr | 79.9163790(16) | Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 684.16 | 2.28 |
| 81Kr | 80.9165920(21) | 210000 y | EC to 81Br | 7/2+ | N/A | 692.24 | - |
| 82Kr | 81.9134836(19) | Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 703.11 | 11.58 |
| 83Kr | 82.914136(3) | Stable | - | 9/2+ | -0.970669 | 710.26 | 11.49 |
| 84Kr | 83.911507(3) | Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 721.13 | 57 |
| 85Kr | 84.9125273(21) | 10.73 y | ß- to 85Rb | 9/2+ | 1.005 | 728.28 | - |
| 86Kr | 85.91061073(11) | Observationally Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 738.22 | 17.3 |
| 87Kr | 86.91335486(29) | 1.27 h | ß- to 87Rb | 5/2+ | -1.018 | 743.51 | - |
| 88Kr | 87.914447(14) | 2.84 h | ß- to 88Rb | 0+ | N/A | 750.65 | - |
| 89Kr | 88.91763(6) | 3.15 min | ß- to 89Rb | 3/2(+#) | N/A | 755.94 | - |
| 90Kr | 89.919517(20) | 32.32(9) s | ß- to 90Rb | 0+ | N/A | 762.15 | - |
| 91Kr | 90.92345(6) | 8.57(4) s | ß- to 91Rb | 5/2(+) | N/A | 766.5 | - |
| 92Kr | 91.926156(13) | 1.840(8) s | ß- to 92Rb; ß- + n to 91Rb | 0+ | N/A | 771.79 | - |
| 93Kr | 92.93127(11) | 1.286(10) s | ß- to 93Rb; ß- + n to 92Rb | 1/2+ | N/A | 775.21 | - |
| 94Kr | 93.93436(32)# | 210(4) ms | ß- to 94Rb; ß- + n to 93Rb | 0+ | N/A | 780.49 | - |
| 95Kr | 94.93984(43)# | 114(3) ms | ß- to 95Rb | 1/2(+) | N/A | 783.91 | - |
| 96Kr | 95.94307(54)# | 80(7) ms | ß- to 96Rb | 0+ | N/A | 788.26 | - |
| 97Kr | 96.94856(54)# | 63(4) ms | ß- to 97Rb; ß- + n to 96Rb | 3/2+# | N/A | 791.69 | - |
| 98Kr | 97.95191(64)# | 46(8) ms | Unknown | 0+ | N/A | 796.97 | - |
| 99Kr | 98.95760(64)# | 40(11) ms | Unknown | (3/2+)# | N/A | 799.46 | - |
| 100Kr | 99.96114(54)# | 10# ms [>300 ns] | Unknown | 0+ | N/A | 803.81 | - |
| 100Kr | 100 | >635 ns | ß- + 2n to 99Rb; ß- + n to 100Rb; ß- to 101Rb; | N/A | N/A | N/A | - |