SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
Product Name: Cobalt Oxide Pellets
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. CO-OX-02-PE
, CO-OX-03-PE
, CO-OX-04-PE
, CO-OX-05-PE
CAS #: 1308-06-1
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Classification of the substance or mixture
GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS)
Respiratory sensitisation(Category 1), H334
Skin sensitisation(Category 1), H317
Carcinogenicity(Category 1A), H350
Acute aquatic toxicity(Category 3), H402
Chronic aquatic toxicity(Category 3), H412
GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements
Pictogram

Signal word
Danger
Hazard statement(s)
H317
May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H334
May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled.
H350
May cause cancer.
H412
Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
P201
Obtain special instructions before use.
P202
Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.
P261
Avoid breathing dust/ fume/ gas/ mist/ Vapors/ spray.
P272
Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
P273
Avoid release to the environment.
P280
Wear protective gloves/ protective clothing/ eye protection/ face protection.
P285
In case of inadequate ventilation wear respiratory protection.
P302 + P352
IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water.
P304 + P341
IF INHALED: If breathing is difficult, remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
P308 + P313
IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/ attention.
P333 + P313
If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/ attention.
P363
Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
P405
Store locked up.
P501
Dispose of contents/ container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Hazards not otherwise classified (HNOC) or not covered by GHS-none
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Substances
Formula: Co3O4
Molecular weight: 240.80 g/mol
CAS-No.: 1308-06-1
Component
Tricobalt tetraoxide
Classification
Resp. Sens.1; Aquatic Acute 3; Aquatic Chronic 3; H334, H412
Concentration
<=100%
Component
Nickel monoxide
Classification
Skin Sens.1; Carc.1A; STOT RE1; Aquatic Chronic 4; H317, H350, H372, H413
Concentration
>=0.1-<1%
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Description of first aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
Move out of dangerous area.
If inhaled
If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. Consult a physician.
In case of skin contact
Wash off with soap and plenty of water. Consult a physician.
In case of eye contact
Flush eyes with water as a precaution.
If swallowed
Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. Consult a physician.
Most important symptoms and effects, both acute and delayed
The most important known symptoms and effects are described in the labelling (see section 2) and/or in section 11
Indication of any immediate medical attention and special treatment needed
No data available
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
Use water spray, alcohol resistant foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
Special hazards arising from the substance or mixture
Cobalt/cobalt oxides
Advice for firefighters
Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
Further information
No data available
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing Vapors, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust.
For personal protection see section 8.
Environmental precautions
Prevent further leakage or spillage if safe to do so. Do not let product enter drains. Discharge into the environment must be avoided.
Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
Pick up and arrange disposal without creating dust. Sweep up and shovel. Keep in suitable, closed containers for disposal.
Reference to other sections
For disposal see section 13.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols.
Further processing of solid materials may result in the formation of combustible dusts. The potential for combustible dust formation should be taken into consideration before additional processing occurs.
Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed.
For precautions see section 2.
Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place.
hygroscopic Keep in a dry place.
Storage class (TRGS 510): Non-combustible, acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
Specific end use(s)
Apart from the uses mentioned in section 1 no other specific uses are stipulated
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
Exposure controls
Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
Personal protective equipment
Eye/face protection
Face shield and safety glasses Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique (without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands.
Full contact
Material: Nature latex/chloroprene
Minimum layer thickness: 0.6 mm
Break through time: > 480 min
Splash contact
Material: Nature latex/chloroprene
Minimum layer thickness: 0.6 mm
Break through time: > 480 min
EN374
If used in solution, or mixed with other substances, and under conditions which differ from EN 374, contact the supplier of the CE approved gloves.
This recommendation is advisory only and must be evaluated by an industrial hygienist and safety officer familiar with the specific situation of anticipated use by our customers. It should not be construed as offering an approval for any specific use scenario.
Body Protection
Complete suit protecting against chemicals, The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace.
Respiratory protection
Where risk assessment shows air-purifying respirators are appropriate use a full-face particle respirator type N100 (US) or type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges as a backup to engineering controls. If the respirator is the sole means of protection, use a full-face supplied air respirator. Use respirators and components tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or CEN (EU).
Control of environmental exposure
Prevent further leakage or spillage if safe to do so. Do not let product enter drains. Discharge into the environment must be avoided.
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Information on basic physical and chemical properties
Appearance
Form: Powder or solid in various forms
Colour: black
Odor
No data available
Odor Threshold
No data available
pH
No data available
Melting point/freezing point
Melting point/range: 895 °C (1,643 °F)-lit.
Initial boiling point and boiling range
No data available
Flash point
No data available
Evaporation rate
No data available
Flammability (solid, gas)
No data available
Upper/lower flammability or explosive limits
No data available
Vapor pressure
No data available
Vapor density
No data available
Relative density
6.11 g/mL at 25 °C (77 °F)
Water solubility
0.00156 g/l at 20 °C (68 °F)-OECD Test Guideline 105-slightly soluble
Partition coefficient: n-octanol/water
No data available
Auto-ignition temperature
No data available
Decomposition temperature
> 900 °C (> 1,652 °F)-
Viscosity
No data available
Explosive properties
No data available
Oxidizing properties
No data available
Other safety information
Bulk density
0.78 g/l
SECTION 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Reactivity
No data available
Chemical stability
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
Possibility of hazardous reactions
No data available
Conditions to avoid
Avoid moisture.
Incompatible materials
Reducing agents
Hazardous decomposition products
Other decomposition products-No data available
In the event of fire: see section 5
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Information on toxicological effects
Acute toxicity
LD50 Oral-Rat-male and female-> 5,000 mg/kg(OECD Test Guideline 401)
LC50 Inhalation-Rat-4 h-> 5.06 mg/l(OECD Test Guideline 436)
LD50 Dermal-Rat-male and female-> 2,000 mg/kg(OECD Test Guideline 402)
No data available
Skin corrosion/irritation
Skin-Rat
Result: No skin irritation
Serious eye damage/eye irritation
Eyes-Rabbit
Result: No eye irritation
(OECD Test Guideline 405)
Respiratory or skin sensitisation
in vivo assay-Mouse
Result: Does not cause skin sensitisation.
(OECD Test Guideline 429)
Germ cell mutagenicity
No data available
in vitro assay
mouse lymphoma cells
Result: negative
OECD Test Guideline 475
Rat-male and female
Result: negative
Carcinogenicity
IARC:
1-Group 1: Carcinogenic to humans(Nickel monoxide)
NTP:
Known to be human carcinogen(Nickel monoxide)
OSHA:
No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as a carcinogen or potential carcinogen by OSHA.
Reproductive toxicity
No data available
Specific target organ toxicity -single exposure
No data available
Specific target organ toxicity -repeated exposure
No data available
Aspiration hazard
No data available
Additional Information
RTECS: Not available
Effects due to ingestion may include:, Burning pain in mouth, throat and stomach., Prolonged or repeated exposure may cause:, Fatigue, Cardiac irregularities, Convulsions, Vomiting.
Stomach-Irregularities-Based on Human Evidence
Stomach-Irregularities-Based on Human Evidence
Stomach-Irregularities-Based on Human Evidence(Nickel monoxide)
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Toxicity
Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates
EC50-Daphnia magna (Water flea)-> 136 mg/l-48 h
Toxicity to algae
EC50-Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata (green algae)-88 mg/l-72 h
Persistence and degradability
No data available
Bioaccumulative potential
Mobility in soil
No data available
Results of PBT and vPvB assessment
PBT/vPvB assessment not available as chemical safety assessment not required/not conducted
Other adverse effects
An environmental hazard cannot be excluded in the event of unprofessional handling or disposal.
Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Waste treatment methods
Product
Offer surplus and non-recyclable solutions to a licensed disposal company.
Contact a licensed professional waste disposal service to dispose of this material.
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber.
Contaminated packaging
Dispose of as unused product.
SECTION 14. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
DOT (US)
Not dangerous goods
IMDG
Not dangerous goods
IATA
Not dangerous goods
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
SARA 302 Components
No chemicals in this material are subject to the reporting requirements of SARA Title III, Section 302.
SARA 313 Components
The following components are subject to reporting levels established by SARA Title III, Section 313:
Nickel monoxide
CAS-No.
1313-99-1
Revision Date
1993-04-24
Tricobalt tetraoxide
1308-06-1
Massachusetts Right To Know Components
Nickel monoxide
CAS-No.
1313-99-1
Revision Date
1993-04-24
California Prop. 65
Components
WARNING! This product contains a chemical known to the State of California to cause cancer.
Nickel monoxide
CAS-No.
1313-99-1
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.
 and smallest possible average grain sizes for use in semiconductor, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes including Thermal and Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation, Low Temperature Organic Evaporation, Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD),
and smallest possible average grain sizes for use in semiconductor, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes including Thermal and Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation, Low Temperature Organic Evaporation, Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), 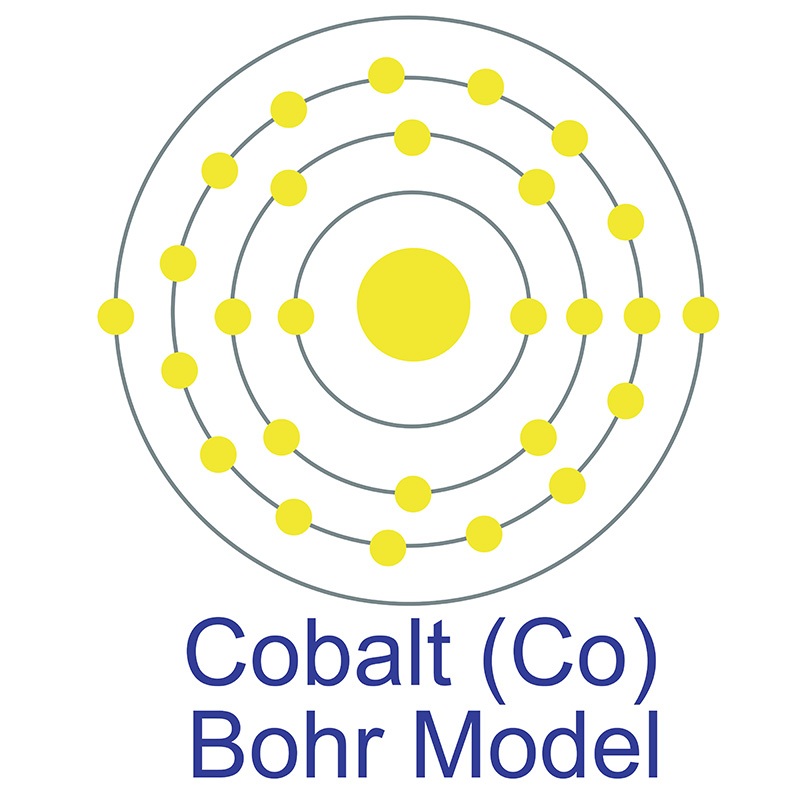 The number of electrons in each of cobalt's shells is 2, 8, 15, 2 and its electron configuration is [Ar]3d7 4s2. The cobalt atom has a radius of 125 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 192 pm. Cobalt was first discovered by George Brandt in 1732. In its elemental form, cobalt has a lustrous gray appearance. Cobalt is found in cobaltite, erythrite, glaucodot and skutterudite ores.
The number of electrons in each of cobalt's shells is 2, 8, 15, 2 and its electron configuration is [Ar]3d7 4s2. The cobalt atom has a radius of 125 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 192 pm. Cobalt was first discovered by George Brandt in 1732. In its elemental form, cobalt has a lustrous gray appearance. Cobalt is found in cobaltite, erythrite, glaucodot and skutterudite ores.  Cobalt produces brilliant blue pigments which have been used since ancient times to color paint and glass. Cobalt is a ferromagnetic metal and is used primarily in the production of
Cobalt produces brilliant blue pigments which have been used since ancient times to color paint and glass. Cobalt is a ferromagnetic metal and is used primarily in the production of