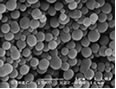
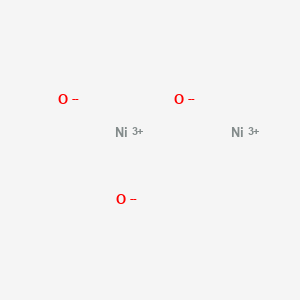
SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
Product Name: Nickel(III) Oxide Nanoparticles / Nanopowder
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. NI3-OX-02-NP
, NI3-OX-03-NP
, NI3-OX-04-NP
, NI3-OX-05-NP
CAS #: 1314-06-3
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Hazard classification
Health hazards
Skin sensitizer
Category 1
Carcinogenicity
Category 1A
Specific target organ toxicity - repeated exposure
Category 1


Signal word: Danger
Hazard statement:
H317 May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H350 May cause cancer.
H372 Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure.
Precautionary statements
Prevention:
P201+P202+P260+P280+P272+P264 Obtain special instructions before use. Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray. Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
P270 Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product.
Response:
P308+P313 IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention.
P302+352-P333+P313+P362+P364-P314 IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water. If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. Take off contaminated clothing and wash before reuse.
Specific treatment (see this label). Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
Storage:
P405 Store locked up.
Disposal:
P501 Dispose of contents/container to an appropriate treatment and disposal facility in accordance with applicable laws and regulations, and product characteristics at time of disposal.
Other hazards which do not result in GHS classification: None.
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Substances
Synonyms: Nickel (III) Oxide; Nickel Oxide; Nickel Sesquioxide; Nickel Peroxide; Nickel Trioxide; Nickel Oxide, Black
CAS No.: 1314-06-3
Molecular Weight: 165.39
Chemical Formula: Ni2O3
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
General information:
Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
Ingestion:
Rinse mouth thoroughly. Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell.
Inhalation:
Move to fresh air. Get medical attention if symptoms persist.
Skin contact:
Wash skin thoroughly with soap and water. If skin irritation or an allergic skin reaction develops, get medical attention. Wash contaminated clothing before reuse. Destroy or thoroughly clean contaminated shoes.
Eye contact:
Immediately flush with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. If easy to do, remove contact lenses. Get medical attention if symptoms persist. Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayed
Symptoms:
May cause irritation to skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled. Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed
Treatment:
Treat symptomatically. Symptoms may be delayed.
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
Fire:
Not considered to be a fire hazard.
Explosion:
Not considered to be an explosion hazard.
Fire Extinguishing Media:
Use any means suitable for extinguishing surrounding fire.
Special Information:
In the event of a fire, wear full protective clothing and NIOSH-approved self-contained breathing apparatus with
full facepiece operated in the pressure demand or other positive pressure mode.
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Ventilate area of leak or spill. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment as specified in Section 8. Spills:
Sweep up and containerize for reclamation or disposal. Vacuuming or wet sweeping may be used to avoid dust
dispersal.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Keep in a tightly closed container, stored in a cool, dry, ventilated area. Protect against physical damage. Wear
special protective equipment (Sec. 8) for maintenance break-in or where exposures may exceed established
exposure levels. Wash hands, face, forearms and neck when exiting restricted areas. Shower, dispose of outer
clothing, change to clean garments at the end of the day. Avoid cross-contamination of street clothes. Wash
hands before eating and do not eat, drink, or smoke in workplace. Containers of this material may be hazardous
when empty since they retain product residues (dust, solids); observe all warnings and precautions listed for the
product.
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
Airborne Exposure Limits:
For Nickel, Metal and Insoluble Compounds, as Ni:
- OSHA Permissible Exposure Limits (PEL) -
1 mg/m3 (TWA).
For Nickel, Elemental / Metal:
- ACGIH Threshold Limit Value (TLV) -
1.5 mg/m3 (TWA), A5 - Not suspected as a human carcinogen.
For Nickel, Insoluble Compounds, as Ni:
- ACGIH Threshold Limit Value (TLV) -
0.2 mg/m3 (TWA), A1 - Confirmed human carcinogen
Ventilation System:
A system of local and/or general exhaust is recommended to keep employee exposures below the Airborne
Exposure Limits. Local exhaust ventilation is generally preferred because it can control the emissions of the
contaminant at its source, preventing dispersion of it into the general work area. Please refer to the ACGIH
document, Industrial Ventilation, A Manual of Recommended Practices, most recent edition, for details.
Personal Respirators (NIOSH Approved):
If the exposure limit is exceeded and engineering controls are not feasible, a half facepiece particulate respirator
(NIOSH type N95 or better filters) may be worn for up to ten times the exposure limit or the maximum use
concentration specified by the appropriate regulatory agency or respirator supplier, whichever is lowest.. A
full-face piece particulate respirator (NIOSH type N100 filters) may be worn up to 50 times the exposure limit,
or the maximum use concentration specified by the appropriate regulatory agency, or respirator supplier,
whichever is lowest. If oil particles (e.g. lubricants, cutting fluids, glycerine, etc.) are present, use a NIOSH type
R or P filter. For emergencies or instances where the exposure levels are not known, use a full-facepiece
positive-pressure, air-supplied respirator. WARNING: Air-purifying respirators do not protect workers in
oxygen-deficient atmospheres.
Skin Protection:
Wear impervious protective clothing, including boots, gloves, lab coat, apron or coveralls, as appropriate, to
prevent skin contact.
Eye Protection:
Use chemical safety goggles and/or full face shield where dusting or splashing of solutions is possible. Maintain
eye wash fountain and quick-drench facilities in work area.
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Appearance: Gray-black powder.
Odor: Odorless.
Solubility: Insoluble in water.
Specific Gravity: 4.84
pH: No information found.
% Volatiles by volume @ 21C (70F): 0
Boiling Point: No information found.
Melting Point: Decomposes at ca. 600C into NiO and oxygen.
Vapor Density (Air=1):
N/A Vapor Pressure (mm Hg): N/A
Evaporation Rate (BuAc=1): No information found.
SECTION 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Stability:
Stable under ordinary conditions of use and storage.
Hazardous Decomposition Products:
Decomposes into nickel monoxide and oxygen.
Hazardous Polymerization:
Will not occur.
Incompatibilities:
Increases the sensitivity of nitroalkanes to heat. Hazardous reaction with hydrogen peroxide.
Conditions to Avoid:
Incompatibles.
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
No LD50/LC50 information found relating to normal routes of occupational exposure. Investigated as a
tumorigen and mutagen.
--------\Cancer Lists\------------------------------------------------------
---NTP Carcinogen---
Ingredient Known Anticipated IARC Category
------------------------------------ ----- ----------- -------------
Nickel Oxide (1314-06-3) No Yes 1
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Environmental Fate:
No information found.
Environmental Toxicity:
No information found.
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Whatever cannot be saved for recovery or recycling should be managed in an appropriate and approved waste
disposal facility. Processing, use or contamination of this product may change the waste management options.
State and local disposal regulations may differ from federal disposal regulations. Dispose of container and
unused contents in accordance with federal, state and local requirements.
SECTION 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
Not Regulated.
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
--------\Chemical Inventory Status - Part 1\---------------------------------
Ingredient TSCA EC Japan Australia
----------------------------------------------- ---- --- ----- ---------
Nickel Oxide (1314-06-3) Yes Yes Yes Yes
--------\Chemical Inventory Status - Part 2\---------------------------------
--Canada--
Ingredient Korea DSL NDSL Phil.
----------------------------------------------- ----- --- ---- -----
Nickel Oxide (1314-06-3) Yes Yes No No
--------\Federal, State & International Regulations - Part 1\----------------
-SARA 302- ------SARA 313------
Ingredient RQ TPQ List Chemical Catg.
----------------------------------------- --- ----- ---- --------------
Nickel Oxide (1314-06-3) No No No Nickel compo
--------\Federal, State & International Regulations - Part 2\----------------
-RCRA- -TSCAIngredient
CERCLA 261.33 8(d)
----------------------------------------- ------ ------ ------
Nickel Oxide (1314-06-3) No No No
Chemical Weapons Convention: No TSCA 12(b): No CDTA: No
SARA 311/312: Acute: Yes Chronic: Yes Fire: No Pressure: No
Reactivity: No (Pure / Solid)
WARNING:
THIS PRODUCT CONTAINS A CHEMICAL(S) KNOWN TO THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA TO CAUSE
CANCER.
Australian Hazchem Code: None allocated.
Poison Schedule: None allocated.
WHMIS:
This MSDS has been prepared according to the hazard criteria of the Controlled Products Regulations (CPR) and the MSDS contains all of the information required by the CPR.
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.
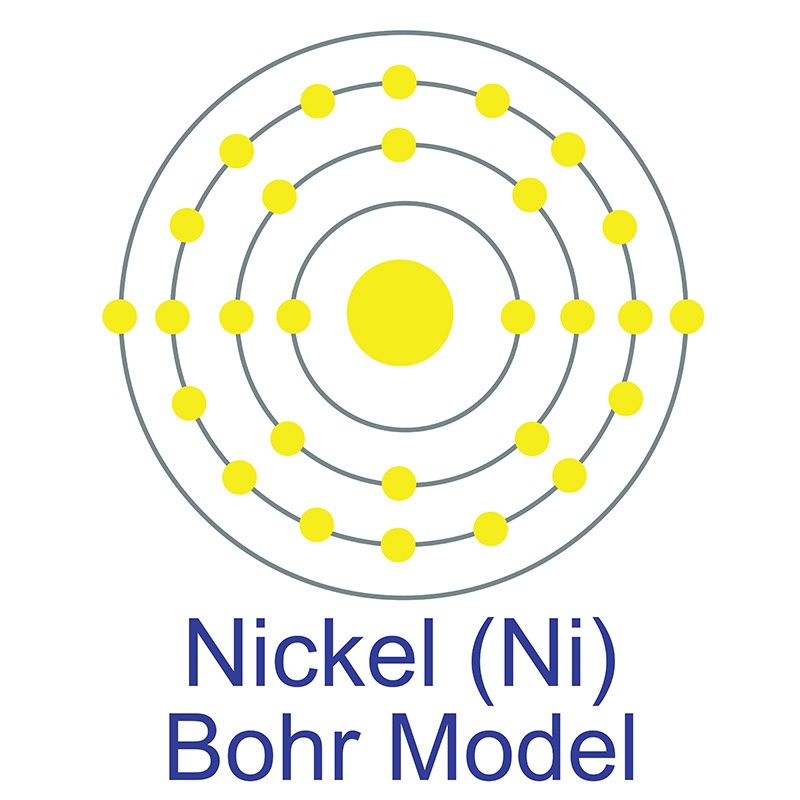 The number of electrons in each of nickel's shells is [2, 8, 16, 2] and its electron configuration is [Ar]3d8 4s2. Nickel was first discovered by Alex Constedt in 1751. The nickel atom has a radius of 124 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 184 pm. In its elemental form, nickel has a lustrous metallic silver appearance. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal that is considered corrosion-resistant because of its slow rate of oxidation.
The number of electrons in each of nickel's shells is [2, 8, 16, 2] and its electron configuration is [Ar]3d8 4s2. Nickel was first discovered by Alex Constedt in 1751. The nickel atom has a radius of 124 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 184 pm. In its elemental form, nickel has a lustrous metallic silver appearance. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal that is considered corrosion-resistant because of its slow rate of oxidation.  It is one of four elements that are ferromagnetic and is used in the production of various type of magnets for commercial use. Nickel is sometimes found free in nature but is more commonly found in ores. The bulk of mined nickel comes from laterite and magmatic sulfide ores. The name originates from the German word kupfernickel, which means "false copper" from the illusory copper color of the ore.
It is one of four elements that are ferromagnetic and is used in the production of various type of magnets for commercial use. Nickel is sometimes found free in nature but is more commonly found in ores. The bulk of mined nickel comes from laterite and magmatic sulfide ores. The name originates from the German word kupfernickel, which means "false copper" from the illusory copper color of the ore.