About Nickel
Despite being extremely common, nickel spent centuries of human history narrowly escaping recognition as a unique metal. As a component of the meteorites that were the only source of iron before its extraction from ore was commonplace, nickel was found in every iron object produced prior to the iron age. As early as 1700 BCE, metalworkers from one Chinese province were highly regarded for paktong, or white copper--a metal smelted from local ores, with a small addition of zinc added for workability--but it was not recognized that the unusual color of the alloy resulted from the high content of a third metal, nickel, in the copper ores. Other ancient societies similarly used naturally occurring copper-nickel ores to produce metal for used for coinage, but also failed to distinguish the metal clearly from pure copper.
It wasn’t until 1751 that Baron Axel Fredrik Cronstedt extracted a white metal from a mineral known as kupfernickel. Frustrated by their inability to extract copper from what they thought was copper ore, medieval German miners had given this mineral its name: kupfer from copper, and nickel from Old Nick, an old name for the devil, whose minions they blamed for their misfortune. Thus, the name Cronstedt gave to his newly discovered metal nickel referenced the host mineral, and by extension, its mythologized demonic origins.
At the time of Baron Cronstedt’s discovery, his new metal was still considered about as useless as the miners had found its native ore, but in 1823, that changed abruptly. Europeans had been importing the Chinese alloy "paktong" (cupronickel) for two centuries, and now finally several German scientists had painstakingly recreated it and developed a functional production process. This European version of cupronickel came to be known as German silver, nickel silver, and by a number of trade names. German silver was valued for its resemblance to silver as well as its hardness and corrosion resistance, and was sought after for both decorative and functional applications, including the production of silverware, musical instruments, plumbing fixtures, and coins. The exact formulation of copper-nickel alloys has varied somewhat over time and by application, but they are still used widely.
Attractive and functional alloys remain the largest use of nickel. Nickel is a key component of some formulations of stainless steel and cast iron, as well as some superalloys designed for use under extreme conditions. Additionally, Alnico alloys containing nickel make strong permanent magnets used in a variety of industrial and consumer applications. Nickel is also widely used as a thin layer plated on other metals through either electroplating or electroless methods. Either form of nickel plating provides increased resistance to wear and corrosion, as nickel is very hard and develops a thin oxide coating upon exposure to air, preventing further corrosion. One key use of the electroless process specifically is in the production of hard-drive disks, where the nickel layer provides an extremely smooth surface in preparation for the deposition of magnetic recording layers.
The other major use for nickel is in batteries and fuel cells. A variety of battery designs, including those exploiting nickel-cadmium, nickel-iron, nickel-hydrogen, and nickel-metal-hydride chemistry, use nickel as a cathode. In alkaline fuel cells, nickel foam or nickel mesh are used as gas diffusion electrodes. Additionally, nickel or nickel alloys such as Raney nickel are used as catalysts in industrial chemistry and organic synthesis, and nickel is sometimes added to glasses or ceramic glazes to produce a bright green color.
Nickel is mined from two types of ore deposits: laterites or magmatic sulfide deposits. The process used to refine nickel involves traditional roasting and reduction of concentrated ores that produce a metal of 75% or greater purity. In some applications such as stainless steel, this relatively low purity may be sufficient and no further requirement is required, but a variety of purification techniques exist to produce higher purity metals. The Mond process has been used since the late nineteenth century to produce nickel metal of 4N purity or higher from nickel oxides.
Products
Nickel is extensively alloyed with iron, chromium, molybdenum, and tungsten to produce stainless steel and other corrosion-resistant alloys. Nickel's high electrical  conductivity lends itself to many electronics applications. For example, it is the basis of the nickel hydride battery and is an ideal component for ceramic anode formulations used in oxygen generation and solid oxide fuel cell applications. Nickel is also used as a pigment; its addition to
conductivity lends itself to many electronics applications. For example, it is the basis of the nickel hydride battery and is an ideal component for ceramic anode formulations used in oxygen generation and solid oxide fuel cell applications. Nickel is also used as a pigment; its addition to  glass and ceramic glazes results in a bright green color. Nickel is available as metal and compounds with purities from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity). Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Nickel nanoparticles and nanopowders are also available. Nickel oxides are available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Nickel fluorides are another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Nickel is also available in soluble forms including chlorides, nitrates and acetates. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
glass and ceramic glazes results in a bright green color. Nickel is available as metal and compounds with purities from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity). Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Nickel nanoparticles and nanopowders are also available. Nickel oxides are available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Nickel fluorides are another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Nickel is also available in soluble forms including chlorides, nitrates and acetates. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
Nickel Properties
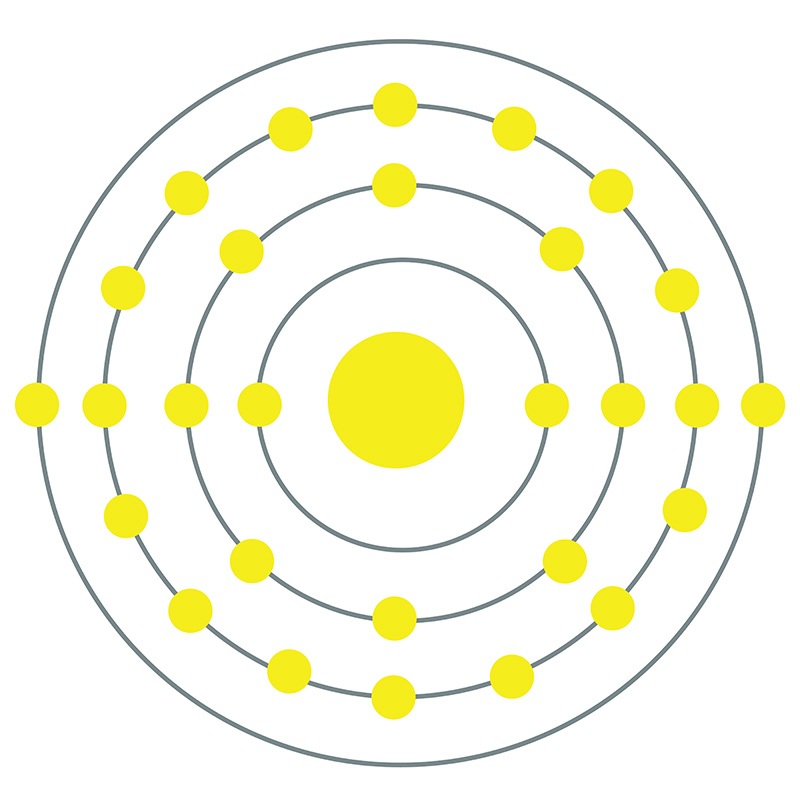
 Nickel is a Block D, Group 4, Period 4 element. The number of electrons in each of nickel's shells is 2, 8, 16, 2 and its electron configuration is [Ar]3d8 4s2.
Nickel is a Block D, Group 4, Period 4 element. The number of electrons in each of nickel's shells is 2, 8, 16, 2 and its electron configuration is [Ar]3d8 4s2. 
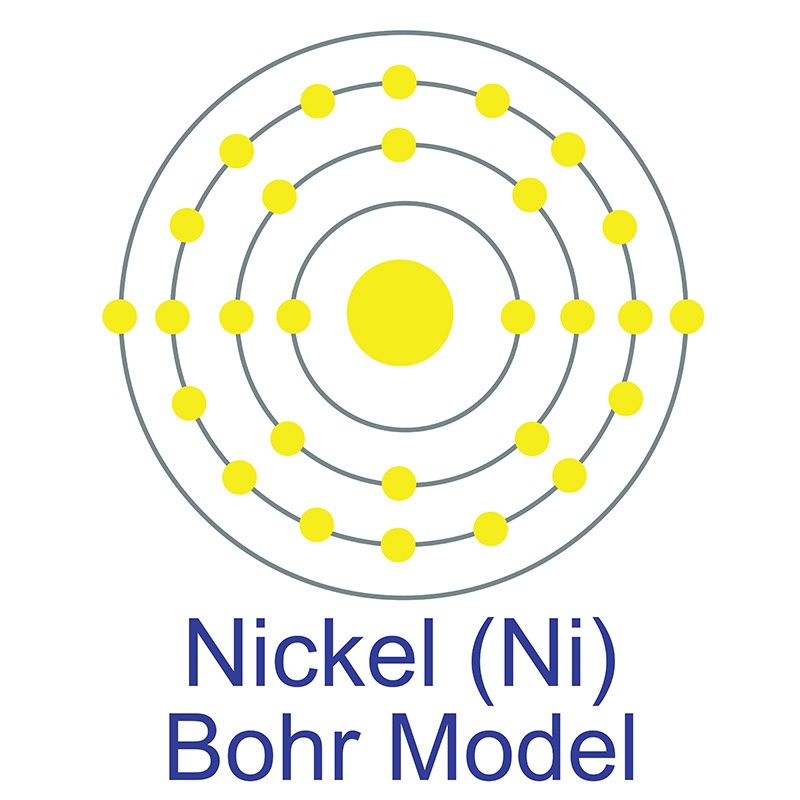 The nickel atom has a radius of 149.pm and its Van der Waals radius is 163.pm. In its elemental form, CAS 7440-02-0, nickel has a lustrous metallic silver appearance. Nickel is sometimes found free in nature but is more commonly found in ores. The bulk of mined nickel comes from laterite and magmatic sulfide ores. Nickel was first discovered by Alex Cronstedt in 1751. The name originates from the German word 'kupfernickel' which means false copper from the illusory copper color of the ore.
The nickel atom has a radius of 149.pm and its Van der Waals radius is 163.pm. In its elemental form, CAS 7440-02-0, nickel has a lustrous metallic silver appearance. Nickel is sometimes found free in nature but is more commonly found in ores. The bulk of mined nickel comes from laterite and magmatic sulfide ores. Nickel was first discovered by Alex Cronstedt in 1751. The name originates from the German word 'kupfernickel' which means false copper from the illusory copper color of the ore.
Health, Safety & Transportation Information for Nickel
Nickel and its compounds are considered to be carcinogenic. Nickel carbonyl is a very toxic gas. Safety data for Nickel and its compounds can vary widely depending on the form. For potential hazard information, toxicity, and road, sea and air transportation limitations, such as DOT Hazard Class, DOT Number, EU Number, NFPA Health rating and RTECS Class, please see the specific material or compound referenced in the Products tab. The below information applies to elemental (metallic) Nickel.
| Safety Data | |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H317-H351-H372-H412 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Codes | 10-40-43 |
| Safety Precautions | 16-36/37 |
| RTECS Number | N/A |
| Transport Information | UN 3089 4.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling (GHS) |
|
Nickel Isotopes
Naturally occurring nickel is composed of five stable isotopes; 58Ni, 60Ni, 61Ni, 62Ni and 64Ni. 58Ni is the most abundant (68.077%).
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48Ni | 48.01975(54)# | 10# ms [>500 ns] | Unknown | 0+ | N/A | 338.66 | - |
| 49Ni | 49.00966(43)# | 13(4) ms [12(+5-3) ms] | Unknown | 7/2-# | N/A | 356.05 | - |
| 50Ni | 49.99593(28)# | 9.1(18) ms | ß+ to 50Cu | 0+ | N/A | 377.18 | - |
| 51Ni | 50.98772(28)# | 30# ms [>200 ns] | ß+ to 51Cu | 7/2-# | N/A | 392.71 | - |
| 52Ni | 51.97568(9)# | 38(5) ms | ß+ to 52Cu; ß+ + p to 51Fe | 0+ | N/A | 411.97 | - |
| 53Ni | 52.96847(17)# | 45(15) ms | ß+ to 53Cu; ß+ + p to 52Fe | (7/2-)# | N/A | 426.57 | - |
| 54Ni | 53.95791(5) | 104(7) ms | ß+ to 54Cu | 0+ | N/A | 444.89 | - |
| 55Ni | 54.951330(12) | 204.7(17) ms | ß+ to 55Cu | 7/2- | N/A | 458.56 | - |
| 56Ni | 55.942132(12) | 6.075(10) d | ß+ to 56Cu | 0+ | N/A | 475.02 | - |
| 57Ni | 56.9397935(19) | 35.60(6) h | EC to 57Co | 3/2- | 0.88 | 485.9 | - |
| 58Ni | 57.9353429(7) | Observationally Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 497.7 | 68.0769 |
| 59Ni | 58.9343467(7) | 7.6(5)E+4 y | EC to 59 Co | 3/2- | N/A | 506.71 | - |
| 60Ni | 59.9307864(7) | STABLE | - | 0+ | N/A | 518.52 | 26.2231 |
| 61Ni | 60.9310560(7) | STABLE | - | 3/2- | -0.75002 | 525.67 | 1.1399 |
| 62Ni | 61.9283451(6) | STABLE | - | 0+ | N/A | 536.54 | 3.6345 |
| 63Ni | 62.9296694(6) | 100.1(20) y | ß- to 63Cu | 1/2- | N/A | 543.69 | - |
| 64Ni | 63.9279660(7) | STABLE | - | 0+ | N/A | 553.63 | 0.9256 |
| 65Ni | 64.9300843(7) | 2.5172(3) h | ß- to 65Cu | 5/2- | 0.69 | 558.91 | - |
| 66Ni | 65.9291393(15) | 54.6(3) h | ß- to 66Cu | 0+ | N/A | 567.92 | - |
| 67Ni | 66.931569(3) | 21(1) s | ß- to 67Cu | 1/2- | N/A | 574.14 | - |
| 68Ni | 67.931869(3) | 29(2) s | ß- to 68Cu | 0+ | N/A | 582.22 | - |
| 69Ni | 68.935610(4) | 11.5(3) s | ß- to 69Cu | 9/2+ | N/A | 586.57 | - |
| 70Ni | 69.93650(37) | 6.0(3) s | ß- to 70Cu | 0+ | N/A | 593.72 | - |
| 71Ni | 70.94074(40) | 2.56(3) s | ß- to 71Cu | 1/2-# | N/A | 598.07 | - |
| 72Ni | 71.94209(47) | 1.57(5) s | ß- to 72Cu; ß- + n to 71Cu | 0+ | N/A | 604.28 | - |
| 73Ni | 72.94647(32)# | 0.84(3) s | ß- to 73Cu; ß- + n to 72Cu | (9/2+) | N/A | 608.64 | - |
| 74Ni | 73.94807(43)# | 0.68(18) s | ß- to 74Cu; ß- + n to 73Cu | 0+ | N/A | 614.85 | - |
| 75Ni | 74.95287(43)# | 0.6(2) s | ß- to 75Cu; ß- + n to 74Cu | (7/2+)# | N/A | 619.2 | - |
| 76Ni | 75.95533(97)# | 470(390) ms [0.24(+55-24) s] | ß- to 76Cu; ß- + n to 75Cu | 0+ | N/A | 624.49 | - |
| 77Ni | 76.96055(54)# | 300# ms [>300 ns] | ß- to 77Cu | 9/2+# | N/A | 627.91 | - |
| 78Ni | 77.96318(118)# | 120# ms [>300 ns] | ß- to 78Cu | 0+ | N/A | 633.19 | - |