SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
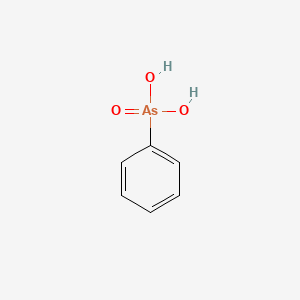
Product Name: Phenylarsonic Acid
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. AS-OMX-01-C
CAS #: 98-05-5
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Classification
This chemical is considered hazardous by the 2012 OSHA Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200)
Acute oral toxicity Category 3
Acute Inhalation Toxicity - Dusts and Mists Category 3
Label Elements

Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Toxic if swallowed or if inhaled
Precautionary Statements
Prevention
Wash face, hands and any exposed skin thoroughly after handling
Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product
Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray
Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area
Inhalation
IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing
Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician
Ingestion
Rinse mouth
IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician
Storage
Store locked up
Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed
Disposal
Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste disposal plant
Hazards not otherwise classified (HNOC)
Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Component
Benzenearsonic acid
CAS-No
98-05-5
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Eye Contact Rinse immediately with plenty of water, also under the eyelids, for at least 15 minutes.
Immediate medical attention is required.
Skin Contact Wash off immediately with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Immediate medical
attention is required.
Inhalation Remove from exposure, lie down. Remove to fresh air. Do not use mouth-to-mouth method if victim ingested or inhaled the substance; give artificial respiration with the aid of a pocket
mask equipped with a one-way valve or other proper respiratory medical device. Immediate
medical attention is required. If not breathing, give artificial respiration.
Ingestion Do NOT induce vomiting. Call a physician or poison control center immediately.
Most important symptoms and effects
No information available.
Notes to Physician Treat symptomatically
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
Suitable Extinguishing Media Water spray. Carbon dioxide (CO 2). Dry chemical. Chemical foam.
Unsuitable Extinguishing Media No information available
Flash Point No information available
Method - No information available
Autoignition Temperature
Explosion Limits
Upper No data available
Lower No data available
Sensitivity to Mechanical Impact No information available
Sensitivity to Static Discharge No information available
Specific Hazards Arising from the Chemical
Do not allow run-off from fire-fighting to enter drains or water courses.
Hazardous Combustion Products
Carbon monoxide (CO). Carbon dioxide (CO2). arsenic oxides.
Protective Equipment and Precautions for Firefighters
As in any fire, wear self-contained breathing apparatus pressure-demand, MSHA/NIOSH (approved or equivalent) and full protective gear.
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal Precautions Ensure adequate ventilation. Use personal protective equipment as required.
Environmental Precautions Do not flush into surface water or sanitary sewer system. Do not allow material to contaminate ground water system. Prevent product from entering drains. Local authorities should be advised if significant spillages cannot be contained. Should not be released into the environment.
Methods for Containment and Clean Up
Wear self-contained breathing apparatus and protective suit. Sweep up and shovel into
suitable containers for disposal. Do not let this chemical enter the environment. Avoid dust
formation. Use spark-proof tools and explosion-proof equipment.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Handling Wear personal protective equipment/face protection. Ensure adequate ventilation. Do not
breathe dust. Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. Do not ingest. If swallowed then
seek immediate medical assistance. Handle product only in closed system or provide
appropriate exhaust ventilation.
Storage Keep in a dry, cool and well-ventilated place. Refer product specification and/or product
label for specific storage temperature requirement. Keep container tightly closed.
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
Exposure Guidelines
Engineering Measures Use only under a chemical fume hood. Ensure that eyewash stations and safety showers are close to the workstation location. Ensure adequate ventilation, especially in confined areas.
Personal Protective Equipment
Eye/face ProtectionWear appropriate protective eyeglasses or chemical safety goggles as described by OSHA's eye and face protection regulations in 29 CFR 1910.133 or European Standard EN 166
Skin and body protection Wear appropriate protective gloves and clothing to prevent skin exposure.
Respiratory Protection Follow the OSHA respirator regulations found in 29 CFR 1910.134 or European Standard EN 149. Use a NIOSH/MSHA or European Standard EN 149 approved respirator if exposure limits are exceeded or if irritation or other symptoms are experienced.
Hygiene Measures Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice.
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Physical State Powder Solid
Appearance Off-white
Odor Odorless
Odor Threshold No information available
pH No information available
Melting Point/Range 160 °C / 320 °F
Boiling Point/Range No information available
Flash Point No information available
Evaporation Rate Not applicable
Flammability (solid,gas) No information available
Flammability or explosive limits
Upper No data available
Lower No data available
Vapor Pressure No information available
Vapor Density Not applicable
Specific Gravity No information available
Solubility slightly soluble
Partition coefficient; n-octanol/water No data available
Autoignition Temperature
Decomposition Temperature > 160°C
Viscosity Not applicable
Molecular Formula C6 H7 As O3
Molecular Weight 202.04
SECTION 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Reactive Hazard None known, based on information available
Stability Stable under normal conditions.
Conditions to Avoid Excess heat. Incompatible products.
Incompatible Materials Strong oxidizing agents
Hazardous Decomposition ProductsCarbon monoxide (CO), Carbon dioxide (CO2), arsenic oxides
Hazardous Polymerization No information available.
Hazardous Reactions None under normal processing.
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Acute Toxicity
Product Information
Component Information
Toxicologically Synergistic
Products
No information available
Delayed and immediate effects as well as chronic effects from short and long-term exposure
Irritation No information available
Sensitization No information available
Mutagenic Effects No information available
Reproductive Effects No information available.
Developmental Effects No information available.
Teratogenicity No information available.
STOT - single exposure None known
STOT - repeated exposure None known
Aspiration hazard No information available
Symptoms / effects,both acute and delayed
No information available
Endocrine Disruptor Information No information available
Other Adverse Effects The toxicological properties have not been fully investigated.
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Ecotoxicity
Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. The product contains following substances which are hazardous for the environment. May cause long-term adverse effects in the environment. Do not allow material to contaminate ground water system.
Persistence and Degradability based on information available. May persist
Bioaccumulation/ Accumulation No information available.
Mobility Will likely be mobile in the environment due to its water solubility.
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Waste Disposal Methods Chemical waste generators must determine whether a discarded chemical is classified as a hazardous waste. Chemical waste generators must also consult local, regional, and national hazardous waste regulations to ensure complete and accurate classification.
SECTION 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
DOT
UN-No UN3465
Proper Shipping Name ORGANOARSENIC COMPOUND, SOLID, N.O.S.
Technical Name (PHENYLARSONIC ACID)
Hazard Class 6.1
Packing Group I
TDG
UN-No UN3465
Proper Shipping Name ORGANOARSENIC COMPOUND, SOLID, N.O.S.
Hazard Class 6.1
Packing Group I
IATA
UN-No UN3465
Proper Shipping Name ORGANOARSENIC COMPOUND, SOLID, N.O.S.
Hazard Class 6.1
Packing Group I
IMDG/IMO
UN-No UN3465
Proper Shipping Name ORGANOARSENIC COMPOUND, SOLID, N.O.S.
Hazard Class 6.1
Packing Group I
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
SARA 302 Components
This material does not contain any components with a section 302 EHS TPQ.
SARA 313 Components
This material does not contain any chemical components with known CAS numbers that
exceed the threshold (De Minimis) reporting levels established by SARA Title III, Section
313.
SARA 311/312 Hazards
Acute Health Hazard, Chronic Health Hazard
Massachusetts Right To Know Components
No components are subject to the Massachusetts Right to Know Act.
Pennsylvania Right To Know Components
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.
 The number of electrons in each of arsenic's shells is 2, 8, 18, 5 and its electron configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3. The arsenic atom has a radius of 119 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 185 pm. Arsenic was discovered in the early Bronze Age, circa 2500 BC. It was first isolated by Albertus Magnus in 1250 AD. In its elemental form, arsenic is a metallic grey, brittle, crystalline, semimetallic solid.
The number of electrons in each of arsenic's shells is 2, 8, 18, 5 and its electron configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3. The arsenic atom has a radius of 119 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 185 pm. Arsenic was discovered in the early Bronze Age, circa 2500 BC. It was first isolated by Albertus Magnus in 1250 AD. In its elemental form, arsenic is a metallic grey, brittle, crystalline, semimetallic solid.  Arsenic is found in numerous minerals including arsenolite (As2O3), arsenopyrite (FeAsS), loellingite (FeAs2), orpiment (As2S3), and realgar (As4S4). Arsenic has numerous applications as a
Arsenic is found in numerous minerals including arsenolite (As2O3), arsenopyrite (FeAsS), loellingite (FeAs2), orpiment (As2S3), and realgar (As4S4). Arsenic has numerous applications as a