See more Cadmium products. Cadmium (atomic symbol: Cd, atomic number: 48) is a Block D, Group 12, Period 5 element with an atomic weight of 112.411.  The number of electrons in each of Cadmium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 18, 2 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d10 5s2. The cadmium atom has a radius of 151 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 230 pm. Cadmium was discovered and first isolated by Karl Samuel Leberecht Hermann and Friedrich Stromeyer in 1817. In its elemental form, cadmium has a silvery bluish gray metallic appearance. Cadmium makes up about 0.1 ppm of the earth's crust.
The number of electrons in each of Cadmium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 18, 2 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d10 5s2. The cadmium atom has a radius of 151 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 230 pm. Cadmium was discovered and first isolated by Karl Samuel Leberecht Hermann and Friedrich Stromeyer in 1817. In its elemental form, cadmium has a silvery bluish gray metallic appearance. Cadmium makes up about 0.1 ppm of the earth's crust.  No significant deposits of cadmium containing ores are known, however, it is sometimes found in its metallic form. It is a common impurity in zinc ores and is isolated during the production of zinc. Cadmium is a key component in battery production and particular pigments and coatings due to its distinct yellow color. Cadmium oxide is used in phosphors for television picture tubes. The name Cadmium originates from the Latin word 'cadmia' and the Greek word 'kadmeia'.
No significant deposits of cadmium containing ores are known, however, it is sometimes found in its metallic form. It is a common impurity in zinc ores and is isolated during the production of zinc. Cadmium is a key component in battery production and particular pigments and coatings due to its distinct yellow color. Cadmium oxide is used in phosphors for television picture tubes. The name Cadmium originates from the Latin word 'cadmia' and the Greek word 'kadmeia'.
Materials
Materials by Form
2D Materials Alloy & Alloy Forms Pure Metals & Metal FormsCeramic FibersFoams: Metallic & Ceramic High Purity Materials Isotopes MXenesOxides Rare Earths Semiconductors Solutions
Chemicals & Salts
All Chemicals & Salts Acetates Aluminides Ammonium Sulfates Antimonides Arsenates Benzoate Bromates Bromides Carbonates Chlorides Chromates Fluorides Hydrides Hydroxides Iodates Iodides Lactates Molybdates Nitrates Oxalates Oxides Perchlorates Phosphates Selenates Selenides Selenites Silicates Stearates Sulfates Sulfides Sulfites Tantalates Tellurates Tellurides Tellurites ThiocyanatesVanadates
Ceramics
Nanomaterials
Organometallics
Materials by Application
Additive Manufacturing & 3D Printing Battery & Supercapacitor Materials Catalysts Dental Materials Electronics Materials Fuel Cell Materials Fusion EnergyGlass Manufacturing Green Technology & Alternative Energy Hydrogen Storage Laser Crystals Life Sciences & Biomaterials Metallurgy Nanotechnology & Nanomaterials Optical Materials Photovoltaic & Solar Energy Plating Pigments & Coatings Research & Development Space Technology Sputtering Targets Thin Film Deposition Water Treatment Weather Modification
Life Science Chemicals
Life Science Products AlcoholsAldehydesAmidesAminesAmino Acids & DerivativesAromaticsArylsAzetidinesBenzimidazolesBenzisoxazolesBenzodioxansBenzofuransBenzothiazolesBenzothiophenesBenzoxazolesCarboxylic AcidsEnzymes & InhibitorsEstersEthersFluorinated Building BlocksFuransHalidesImidazolesImidazolidinesIndazolesIndolesIndolinesIsoquinolinesIsoxazolesKetonesMorpholinesNaphthyridinesNitrilesOrganoboronOrganosiliconOxadiazolesOxazolesPharmaceuticals & IntermediatesPhenolsPhytochemicalsPiperazinesPiperidinesPyrazinesPyrazolesPyridazinesPyridinesPyrimidinesPyrrolesPyrrolidinesPyrrolinesQuinazolinesQuinolinesQuinoxalinesSpiroesSulfonyl ChloridesTetrahydroisoquinolinesTetrahydropyransTetrahydroquinolinesTetrazolesThiadiazolesThiazolesThiazolidinesThiolsThiophenesTriazinesTriazoles
About Us
Locations
Austria Belgium Brazil Canada China & Hong Kong Czech Republic Denmark Finland France Germany Greece Hungary India Indonesia Israel Italy Japan Malaysia Mexico Netherlands Norway Philippines Poland Portugal Russia Singapore South Korea Spain Sweden Switzerland Taiwan Thailand Turkey United Kingdom United States
Industries
Aerospace Agriculture Automotive Chemical Manufacturing Defense Dentistry Electronics Energy Storage & Batteries Fine Art Materials Fuel CellsFusion Energy Glass Investment Grade Metals Jewelry & Fashion Lasers Lighting Medical Devices Museums & Galleries Nuclear Energy Oil & Gas Optics Paper & Pulp Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Research & Laboratory Robotics Solar Energy Space Sports Equipment Steel & Alloy Producers Textiles & Fabrics Water Treatment Municipalities
Follow Us
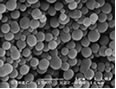 Cadmium Tungstate Nanoparticles, nanodots or
Cadmium Tungstate Nanoparticles, nanodots or  The tungsten atom has a radius of 139 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 210 pm. Tungsten was discovered by Torbern Bergman in 1781 and first isolated by Juan José Elhuyar and Fausto Elhuyar in 1783. In its elemental form, tungsten has a grayish white, lustrous appearance.
The tungsten atom has a radius of 139 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 210 pm. Tungsten was discovered by Torbern Bergman in 1781 and first isolated by Juan José Elhuyar and Fausto Elhuyar in 1783. In its elemental form, tungsten has a grayish white, lustrous appearance.  Tungsten has the highest melting point of all the
Tungsten has the highest melting point of all the