SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
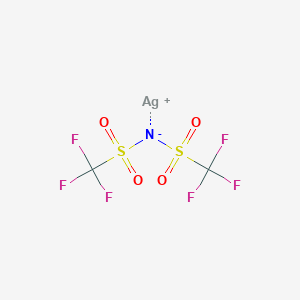
Product Name: Silver Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. AG-FMSI-02
, AG-FMSI-03
, AG-FMSI-04
, AG-FMSI-05
CAS #: 189114-61-2
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
OSHA Haz Com: CFR 1910.1200: Eye Damage/Irritation [Category 1]
Skin Corrosion/Irritation [Category 1C]
Signal word: Danger!
Hazard Statement(s): Causes serious eye damage
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
Pictogram(s) or Symbol(s):
Precautionary Statement(s):
[Prevention] Do not breathe dusts or mists. Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. Wear protective gloves,
protective clothing, eye protection and face protection. Wear eye protection. Wear face protection (full
length face shield).
[Response] If swallowed: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. If on skin (or hair): Take off immediately all
contaminated clothing. Rinse skin with water or shower. Wash contaminated clothing before reuse. If
inhaled: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing. Immediately call a poison center
or doctor. If in eyes: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present
and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
[Storage] Store locked up.
[Disposal] Dispose of contents and container in accordance with US EPA guidelines for the classification and
determination of hazardous waste listed in 40 CFR 261.3. (See Section 13)
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Substance/Mixture: Substance
Components: Silver Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide
Percent: >98.0%(T)
CAS Number: 189114-61-2
Molecular Weight: 388.00
Chemical Formula: C2AgF6NO4S2
Synonyms: Silver Triflimide
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Inhalation: Immediately call a poison center or doctor. Effects of exposure (inhalation) to substance may be delayed.
Move victim to fresh air. Give artificial respiration if victim is not breathing. Administer oxygen if breathing is
difficult. Keep victim warm and quiet. Treat symptomatically and supportively. Ensure that medical
personnel are aware of the material(s) involved and take precautions to protect themselves.
Skin contact: For severe burns, immediate medical attention is required. Immediately call a poison center or doctor.
Remove and wash contaminated clothing before re-use. In case of contact with substance, immediately
flush skin with running water for at least 20 minutes. Treat symptomatically and supportively. Ensure that
medical personnel are aware of the material(s) involved and take precautions to protect themselves.
Eye contact: IMMEDIATELY flush eyes with running water for at least 15 minutes, keeping eyelids open. Eye contact
with vapors or substance may cause severe injury, burns, or death. Call emergency medical service. Move
victim to fresh air. Check for and remove any contact lenses. Keep victim warm and quiet. Treat
symptomatically and supportively. Effects of exposure to substance may be delayed. Ensure that medical
personnel are aware of the material(s) involved and take precautions to protect themselves.
Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting with out medical advice. Call a physician or Poison Control Center immediately. Do
not use mouth-to-mouth method if victim ingested the substance; give artificial respiration with the aid of a
pocket mask equipped with a one-way valve or other proper respiratory medical device. Loosen tight
clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. If a person vomits place them in the recovery position so
that vomit will not reenter the mouth and throat. Rinse mouth. Keep victim warm and quiet. Treat
symptomatically and supportively. Ensure that medical personnel are aware of the material(s) involved and
take precautions to protect themselves.
Symptoms/effects:
Acute: Pain. Redness.
Delayed: No data available
Immediate medical attention: WARNING: It might be hazardous to the person providing aid to give mouth-to-mouth respiration, because
the inhaled material is corrosive. For severe burns, immediate medical attention is required. If breathing
has stopped, perform artificial respiration. Use first aid treatment according to the nature of the injury.
Ensure that medical personnel are aware of the material(s) involved and take precautions to protect
themselves.
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
Suitable extinguishing media: Dry chemical, CO2 or water spray. Consult with local fire authorities before attempting large scale fire
fighting operations.
Specific hazards arising from the chemical
Hazardous combustion products: These products include: Carbon oxides Nitrogen oxides Sulfur oxides Halogenated compounds Metallic
oxides
Other specific hazards: WARNING: Highly toxic HF gas is produced during combustion.
Special precautions for fire-fighters:
Use water spray or fog; do not use straight streams. Dike fire-control water for later disposal; do not scatter the material. Containers may explode when
heated. Move containers from fire area if you can do it without risk.
Special protective equipment for fire-fighters:
Wear positive pressure self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA). Structural fire fighters' protective clothing provides limited protection in fire situations
ONLY; it may not be effective in spill situations. Wear chemical protective clothing which is specifically recommended by the manufacturer. It may
provide little or no thermal protection.
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal precautions: Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing. Keep people away from and upwind of spill/leak. Do not touch
damaged containers or spilled material unless wearing appropriate protective clothing (Section 8). Warn
unnecessary personnel to move away. Stop leak if you can do it without risk. Ensure adequate ventilation.
Isolate the hazard area and deny entry to unnecessary and unprotected personnel.
Personal protective equipment: Wear eye protection (splash goggles) and face protection (full length face shield). Lab coat. Dust
respirator. Be sure to use a MSHA/NIOSH approved respirator or equivalent. Wear protective gloves
(nitrile).
Emergency procedures: Prevent dust cloud. In case of a spill and/or a leak, always shut off any sources of ignition, ventilate the
area, and excercise caution. Do not touch damaged containers or spilled material unless wearing
appropriate protective clothing. Warn personnel to move away. Prevent entry into sewers, basements or
confined areas; dike if needed.
Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up:
ELIMINATE all ignition sources (no smoking, flares, sparks, or flames in immediate area). Stop leak if without risk. Ventilate the area. Absorb with an
inert material and put the spilled material in an appropriate waste disposal container. Use clean non-sparking tools to collect absorbed material.
Environmental precautions:
Prevent further leakage or spillage if safe to do so. Water runoff can cause environmental damage. Prevent entry into sewers, basements or confined
areas; dike if needed.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Precautions for safe handling: Avoid inhalation of vapor or mist. Manipulate under an adequate fume hood. Avoid contact with skin and
eyes. Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to keep airborne
levels below recommended exposure limits. Keep container dry. Handle and open container with care.
Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. When using do not eat, drink, or smoke.
Keep away from sources of ignition.
Conditions for safe storage: Store locked up. Keep containers tightly closed in a cool, well-ventilated place. Keep away from
incompatibles. Containers which are opened must be carefully resealed and kept upright to prevent
leakage. Avoid prolonged storage periods. Store under inert gas (e.g. Argon). Hygroscopic material, store
in a tightly sealed container. Store in a freezer.
Storage incompatibilities: Store away from oxidizing agents
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
ACGIH TLV (TWA): 0.01 mg(Ag)/m3
OSHA PEL (TWA): 0.01 mg(Ag)/m3
Appropriate engineering controls:
Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to keep airborne levels below recommended exposure limits. Ventilation
is normally required when handling or using this product. Eyewash fountains should be provided in areas where there is any possibility that workers
could be exposed to the substance. Follow safe industrial engineering/laboratory practices when handling any chemical.
Personal protective equipment
Respiratory protection: Dust respirator. Be sure to use a MSHA/NIOSH approved respirator or equivalent.
Hand protection: Nitrile gloves.
Eye protection: Safety glasses.
Skin and body protection: Wear protective clothing (lab coat and chemical resistant boots).
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Physical state (20°C): Solid
Form: Crystal - Powder
Color: White - Slightly pale reddish yellow
Odor: No data available
Odor threshold: No data available
Melting point/freezing point: 249°C (480°F)
Boiling point/range: No data available
Decomposition temperature: No data available
Relative density: No data available
Kinematic Viscosity: No data available
Partition coefficient: No data available
n-octanol/water (log Pow)
Flash point: No data available
Flammability (solid, gas): No data available
pH: No data available
Vapor pressure: No data available
Vapor density: No data available
Dynamic Viscosity: No data available
Evaporation rate: No data available
(Butyl Acetate = 1)
Autoignition temperature: No data available
Flammability or explosive limits: No data available
Lower: No data available
Upper: No data available
Solubility(ies):
Water: Soluble
SECTION 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Reactivity: Not Available.
Chemical Stability: Moisture sensitive. Light sensitive.
Possibility of Hazardous Reactions: No hazardous reactivity has been reported.
Conditions to avoid: Exposure to light. Exposure to moisture. Moisture sensitive.
Incompatible materials: Oxidizing agents
Hazardous Decomposition Products: No data available
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Acute Toxicity:
No data available
Skin corrosion/irritation:
No data available
Serious eye damage/irritation:
No data available
Respiratory or skin sensitization:
No data available
Germ cell mutagenicity:
No data available
Carcinogenicity:
No data available
IARC: No data available
NTP: No data available
OSHA: No data available
Reproductive toxicity:
No data available
Routes of Exposure: Inhalation, Eye contact, Ingestion, Skin contact.
Symptoms related to exposure:
Skin contact may produce burrns. Skin contact may result in inflammation; characterized by itching, scaling, reddening, or occasionally blistering. Eye
contact can result in corneal damage or blindness.
Potential Health Effects:
No specific information available; skin and eye contact may result in irriatation. May be harmful if inhaled or ingested.
Target organ(s): No data available
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Ecotoxicity
Fish: No data available
Crustacea: No data available
Algae: No data available
Persistence and degradability: No data available
Bioaccumulative potential (BCF): No data available
Mobillity in soil: No data available
Partition coefficient:
n-octanol/water (log Pow)
No data available
Soil adsorption (Koc): No data available
Henry's Law:
constant (PaM3/mol)
No data available
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Disposal of product: Recycle to process if possible. It is the generator's responsibility to comply with Federal, State and Local
rules and regulations. You may be able to dissolve or mix material with a combustible solvent and burn in a
chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber system. This section is intended to provide
assistance but does not replace these laws, nor does compliance in accordance with this section ensure
regulatory compliance according to the law. US EPA guidelines for Identification and Listing of Hazardous
Waste are listed in 40 CFR Parts 261. The product should not be allowed to enter the environment, drains,
water ways, or the soil.
Disposal of container: Dispose of as unused product. Do not re-use empty containers.
Other considerations: Observe all federal, state and local regulations when disposing of the substance.
SECTION 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
DOT (US)
UN number:
UN1759
Proper Shipping Name:
Corrosive solids, n.o.s.
Class or Division:
8 Corrosive material
Packing Group:
III
IATA
UN number:
UN1759
Proper Shipping Name:
Corrosive solids, n.o.s.
Class or Division:
8 Corrosive material
Packing Group:
III
IMDG
UN number:
UN1759
Proper Shipping Name:
Corrosive solids, n.o.s.
Class or Division:
8 Corrosive material
Packing Group:
III
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
Toxic Substance Control Act (TSCA 8b.):
This product is NOT on the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) inventory. The following notices are required by 40 CFR 720.36 (C) for those
products not on the inventory list:
(i) These products are supplied solely for use in research and development by or under the supervision of a technically qualified individual as defined in
40 CFR 720.0 et sec.
(ii) The health risks of these products have not been fully determined. Any information that is or becomes available will be supplied on a SDS sheet.
US Federal Regulations
CERCLA Hazardous substance and Reportable Quantity:
SARA 313: Not Listed
SARA 302: Not Listed
State Regulations
State Right-to-Know
Massachusetts Not Listed
New Jersey Not Listed
Pennsylvania Not Listed
California Proposition 65: Not Listed
Other Information
NFPA Rating:
Health: 0
Flammability: 0
Instability: 0
HMIS Classification:
Health: 0
Flammability: 0
Physical: 0
International Inventories
WHMIS hazard class: E: Corrosive material.
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.
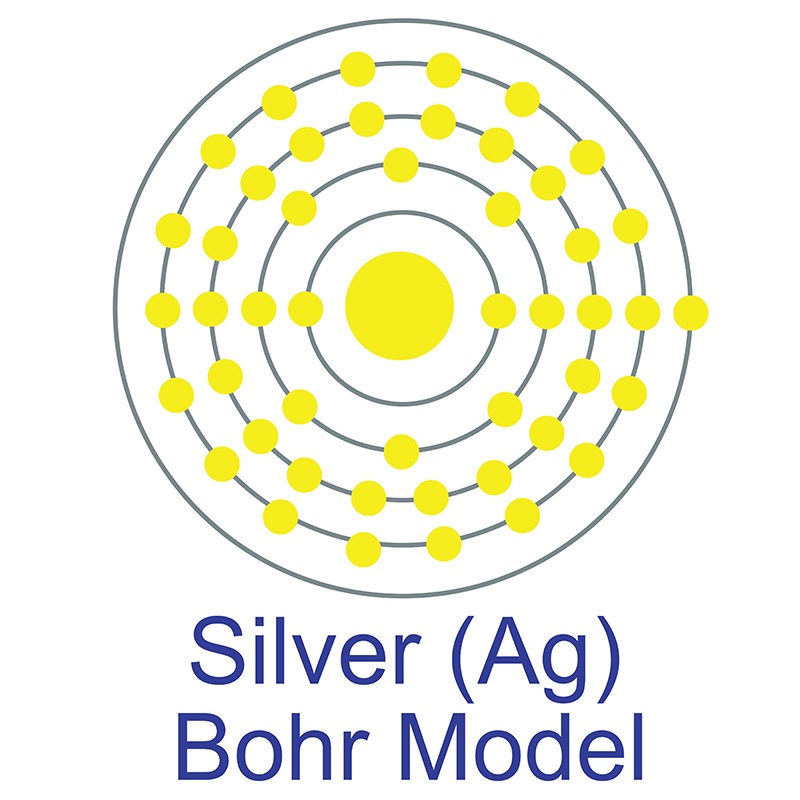 The number of electrons in each of Silver's shells is 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d10 5s1. The silver atom has a radius of 144 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 203 pm. Silver was first discovered by Early Man prior to 5000 BC. In its elemental form, silver has a brilliant white metallic luster.
The number of electrons in each of Silver's shells is 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d10 5s1. The silver atom has a radius of 144 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 203 pm. Silver was first discovered by Early Man prior to 5000 BC. In its elemental form, silver has a brilliant white metallic luster.  It is a little harder than
It is a little harder than 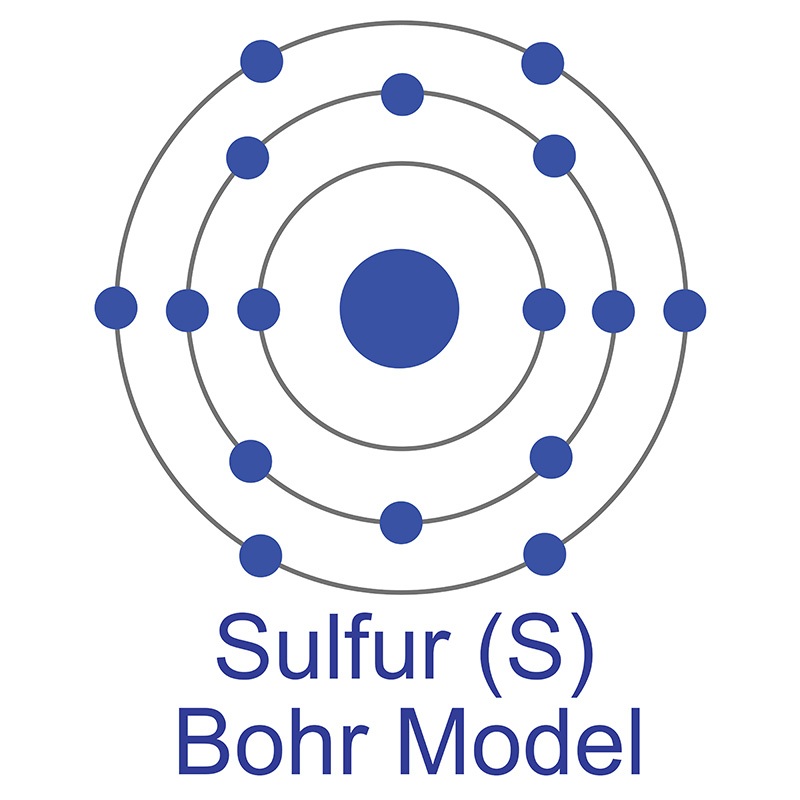 The number of electrons in each of Sulfur's shells is 2, 8, 6 and its electron configuration is [Ne] 3s2 3p4. In its elemental form, sulfur has a light yellow appearance. The sulfur atom has a covalent radius of 105 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 180 pm. In nature, sulfur can be found in hot springs, meteorites, volcanoes, and as galena, gypsum, and epsom salts. Sulfur has been known since ancient times but was not accepted as an element until 1777, when Antoine Lavoisier helped to convince the scientific community that it was an element and not a compound.
The number of electrons in each of Sulfur's shells is 2, 8, 6 and its electron configuration is [Ne] 3s2 3p4. In its elemental form, sulfur has a light yellow appearance. The sulfur atom has a covalent radius of 105 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 180 pm. In nature, sulfur can be found in hot springs, meteorites, volcanoes, and as galena, gypsum, and epsom salts. Sulfur has been known since ancient times but was not accepted as an element until 1777, when Antoine Lavoisier helped to convince the scientific community that it was an element and not a compound.