About Rhodium
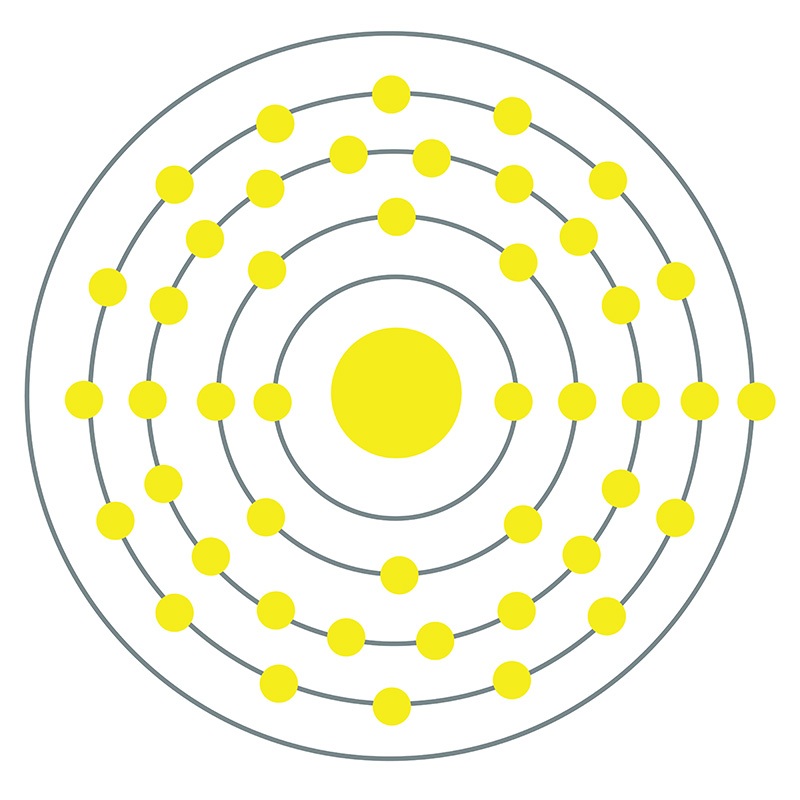
Rhodium is a hard, durable metal with a shiny silver appearance and high resistance to corrosion. It is one of the rarest metals in the Earth’s crust, a factor that, along with its value for many applications, ensures its extremely high cost. The majority of new rhodium produced is used to produce three-way catalytic converters, where it is more efficient than other platinum group elements at reducing nitrogen oxides. Additionally, rhodium-based catalysts are widely used in industrial processes and other organic chemistry applications.
The remaining rhodium is used as an alloying agent that improves the corrosion resistance and increases the hardness of platinum and palladium, or used ornamentally. Rhodium-containing alloys are used in spark plugs, advanced laboratory equipment, and in thermocouples. In jewelry manufacturing, extremely thin layers of the precious metal are electroplated onto white gold or platinum to give a reflective white surface, a process known as “rhodium flashing”.
Platinum first came to Europe as platina, grey metallic crumbs that were unusable to metalworkers in their native form. Initially, few people could convert platina to workable platinum, and the process involved was a carefully guarded secret. The problem with early platina processing had been that the final material produced did not seem to have consistent properties--a problem solved when it was recognized that platina actually included several different metals. William Hyde Wollaston, an English chemist, was the first to isolate rhodium from platina samples and named the element based on the rose-red color of one of its compounds.
Like other platinum group metals, rhodium is typically obtained for commercial use as a byproduct from nickel and copper mining and processing, but can also be obtained from ores rich in platinum and alluvial deposits. Along with ruthenium and palladium, rhodium is a decomposition product of uranium and could theoretically be recovered from spent nuclear fuel, but the problems inherent in working with radioactive materials make this an impractical source for the rare element.
Products
Rhodium is alloyed with platinum and palladium in electrodes for spark plugs, advanced laboratory equipment and in thermocouples. Rhodium compounds also have catalytic uses in automotive catalytic converters.  Rhodium is used as a plating metal in jewelry production to enhance the whiteness of white gold and platinum. Rhodium is available as metal and in compound forms with purities ranging from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity).
Rhodium is used as a plating metal in jewelry production to enhance the whiteness of white gold and platinum. Rhodium is available as metal and in compound forms with purities ranging from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity).  Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Rhodium nanoparticles and nanopowders provide ultra-high surface area. Rhodium oxides is an insoluble rhodium source available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications Rhodium fluoride is another insoluble form of for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Rhodium is also available in soluble forms including chlorides, nitrates and acetates. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Rhodium nanoparticles and nanopowders provide ultra-high surface area. Rhodium oxides is an insoluble rhodium source available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications Rhodium fluoride is another insoluble form of for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Rhodium is also available in soluble forms including chlorides, nitrates and acetates. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
Rhodium Properties
 Rhodium is a Block D, Group 9, Period 5 element.
Rhodium is a Block D, Group 9, Period 5 element. 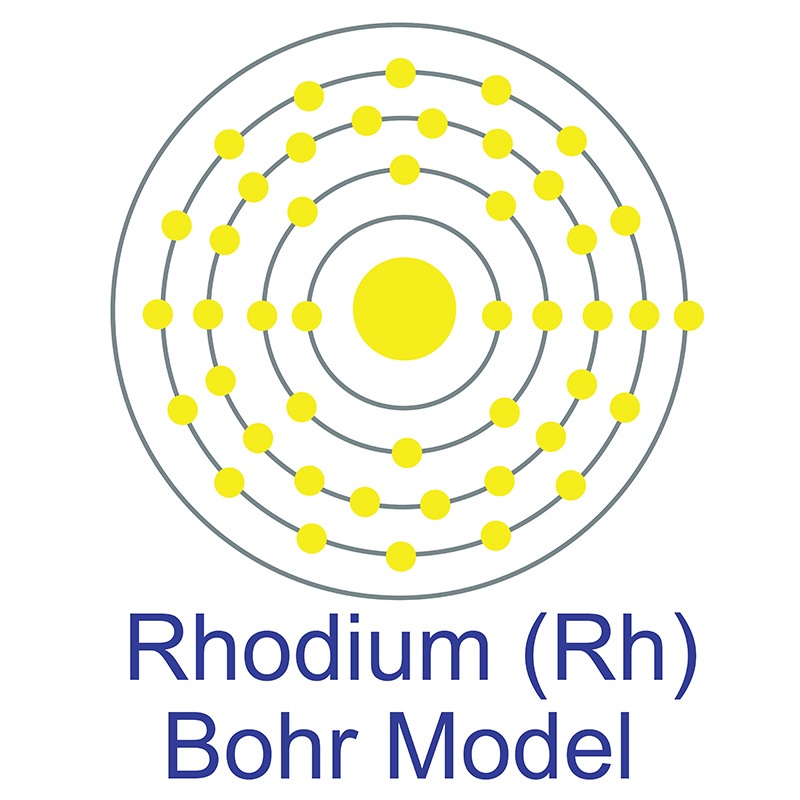 . Rhodium was first discovered by William Wollaston in 1803. The name rhodium originates from the Greek word 'Rhodon,' which means rose.
. Rhodium was first discovered by William Wollaston in 1803. The name rhodium originates from the Greek word 'Rhodon,' which means rose.
Health, Safety & Transportation Information for Rhodium
Rhodium is not toxic in its elemental form; however, safety data for Rhodium and its compounds can vary widely depending on the form. For potential hazard information, toxicity, and road, sea and air transportation limitations, such as DOT Hazard Class, DOT Number, EU Number, NFPA Health rating and RTECS Class, please see the specific material or compound referenced in the Products tab. The below information applies to elemental (metallic) Rhodium.
| Safety Data | |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H228 |
| Hazard Codes | N/A |
| Risk Codes | N/A |
| Safety Precautions | N/A |
| RTECS Number | VI9069000 |
| Transport Information | N/A |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling (GHS) |
|
Rhodium Isotopes
Naturally occurring rhodium (Rh) has one stable isotope: 103Rh.
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 89Rh | 88.94884(48)# | 10# ms [>1.5 µs] | ß+ to 89Ru | 7/2+# | N/A | 716.96 | - |
| 90Rh | 89.94287(54)# | 15(7) ms [12(+9-4) ms] | ß+ to 90Ru | 0+# | N/A | 730.63 | - |
| 91Rh | 90.93655(43)# | 1.74(14) s | ß+ to 91Ru | 7/2+# | N/A | 744.29 | - |
| 92Rh | 91.93198(43)# | 4.3(13) s | ß+ to 92Ru | (6+) | N/A | 757.03 | - |
| 93Rh | 92.92574(43)# | 11.9(7) s | ß+ to 93Ru | 9/2+# | N/A | 770.7 | - |
| 94Rh | 93.92170(48)# | 70.6(6) s | ß+ to 94Ru; ß+ + p to 93Tc | (2+,4+) | N/A | 782.5 | - |
| 95Rh | 94.91590(16) | 5.02(10) min | ß+ to 95Ru | (9/2)+ | N/A | 796.17 | - |
| 96Rh | 95.914461(14) | 9.90(10) min | ß+ to 96Ru | (6+) | N/A | 805.18 | - |
| 97Rh | 96.91134(4) | 30.7(6) min | ß+ to 97Ru | 9/2+ | N/A | 816.06 | - |
| 98Rh | 97.910708(13) | 8.72(12) min | ß+ to 98Ru | (2)+ | N/A | 825.07 | - |
| 99Rh | 98.908132(8) | 16.1(2) d | EC to 99Ru | 1/2- | N/A | 835.01 | - |
| 100Rh | 99.908122(20) | 20.8(1) h | EC to 100Ru | 1- | N/A | 843.09 | - |
| 101Rh | 100.906164(18) | 3.3(3) y | EC to 101Ru; IT | 1/2- | N/A | 858.62 | - |
| 102Rh | 101.906843(5) | 207.0(15) d | EC to 102Ru; ß- to 102Pd | (1-,2-) | 4.04 | 866.7 | - |
| 103Rh | 102.905504(3) | Observationally Stable | - | 1/2- | -0.0884 | 874.78 | 100 |
| 104Rh | 103.906656(3) | 42.3(4) s | EC to 104Ru; ß- to 104Pd | 1+ | N/A | 882.86 | - |
| 105Rh | 104.905694(4) | 35.36(6) h | ß- to 105Pd | 7/2+ | 4.45 | 890.93 | - |
| 106Rh | 105.907287(8) | 29.80(8) s | ß- to 106Pd | 1+ | N/A | 899.01 | - |
| 107Rh | 106.906748(13) | 21.7(4) min | ß- to 107Pd | 7/2+ | N/A | 907.09 | - |
| 108Rh | 107.90873(11) | 16.8(5) s | ß- to 108Pd | 1+ | N/A | 915.17 | - |
| 109Rh | 108.908737(13) | 80(2) s | ß- to 109Pd | 7/2+ | N/A | 923.25 | - |
| 110Rh | 109.91114(5) | 28.5(15) s | ß- to 110Pd | (>3)(+#) | N/A | 922.01 | - |
| 111Rh | 110.91159(3) | 11(1) s | ß- to 111Pd | (7/2+) | N/A | 930.09 | - |
| 112Rh | 111.91439(6) | 3.45(37) s | ß- to 112Pd | 1+ | N/A | 938.17 | - |
| 113Rh | 112.91553(5) | 2.80(12) s | ß- to 113Pd | (7/2+) | N/A | 946.25 | - |
| 114Rh | 113.91881(12) | 1.85(5) s | ß- to 114Pd; ß- + n to 113Pd | 1+ | N/A | 954.33 | - |
| 115Rh | 114.92033(9) | 0.99(5) s | ß- to 115Pd | (7/2+)# | N/A | 953.09 | - |
| 116Rh | 115.92406(15) | 0.68(6) s | ß- to 116Pd; ß- + n to 115Pd | 1+ | N/A | 961.17 | - |
| 117Rh | 116.92598(54)# | 0.44(4) s | ß- to 117Pd | (7/2+)# | N/A | 969.25 | - |
| 118Rh | 117.93007(54)# | 310(30) ms | ß- to 118Pd | (4-10)(+#) | N/A | 968.01 | - |
| 119Rh | 118.93211(64)# | 300# ms [>300 ns] | ß- to 119Pd | 7/2+# | N/A | 976.09 | - |
| 120Rh | 119.93641(64)# | 200# ms [>300 ns] | ß- to 120Pd | N/A | N/A | 984.17 | - |
| 121Rh | 120.93872(97)# | 100# ms [>300 ns] | ß- to 121Pd | 7/2+# | N/A | 992.24 | - |
| 122Rh | 121.94321(75)# | 50# ms [>300 ns] | Unknwon | N/A | N/A | 991.01 | - |