SECTION 1. IDENTIFICATION
Product Name: Silver Chloride
Product Number: All applicable American Elements product codes, e.g. AG-CL-02
, AG-CL-03
, AG-CL-04
, AG-CL-05
CAS #: 7783-90-6
Relevant identified uses of the substance: Scientific research and development
Supplier details:
American Elements
10884 Weyburn Ave.
Los Angeles, CA 90024
Tel: +1 310-208-0551
Fax: +1 310-208-0351
Emergency telephone number:
Domestic, North America: +1 800-424-9300
International: +1 703-527-3887
SECTION 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Harmful by ingestion, inhalation and skin contact. Prolonged exposure may result in argyria, a bluish discolouration of the skin. Irritating to eyes and may irritate skin.
SECTION 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
COMPONENT NAME CAS No. % CLASS HEALTH RISK UN No.
Silver Chloride 7783-90-6 100% N.R. N.R. 22/24-25 -
SECTION 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
GENERAL: Consult a Physician for specific advice
EYES: Irrigate thoroughly with water for at least 10 minutes. Obtain medical attention.
SKIN: Wash off thoroughly with water. Remove contaminated clothing and wash before re-use. In severe cases obtain medical attention.
INHALATION: Remove from exposure, rest and keep warm. In severe cases seek medical attention.
INGESTION: Wash out mouth thoroughly with water and give plenty to drink. Obtain medical attention.
SECTION 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
FLASH POINT: Not Ignitable. Not Applicable
UNUSUAL FIRE HAZARDS: May evolve toxic fumes in a fire.
SECTION 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
CONTAMINATION CLEANUP: Wear suitable protective clothing & equipment as listed under Exposure / Personal protection. Mix with sand, transfer carefully to
container and arrange removal by disposal company. Wash site of spillage thoroughly with water and detergent. For large spillages liquids should be contained with
sand or earth and both liquids and solids transferred to salvage containers. Any residues should be treated as for small spillages.
SECTION 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
USAGE PRECAUTIONS: Wash hands and face thoroughly after working with material. Protect from light.
STORAGE PRECAUTIONS: Store at room temperature (15 to 25oC recommended). Keep well closed and protected from direct sunlight and moisture.
SECTION 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
Protective gloves made of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) are required. Use of a laboratory coat is suggested. Safety goggles or safety glasses with side shields are required if
there is any possibility of chipping or dust creation. Respirators must be worn when the threshold limit is exceeded. Provide adequate general mechanical ventilation, and
local exhaust ventilation. When handling quantities of this material, be sure to wear appropriate protective equipment as described. Eye wash should be readily available.
Wash thoroughly after handling. Do not take internally. Avoid breathing dust when generated. For persons with sensitive existing medical conditions, medical advice
should be sought before employing on tasks involving exposure to this material.
EXPOSURE LIMITS: OES Silver Compounds 0.01mg/m3 (Long term, 8 hour TWA)
SECTION 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
APPEARANCE : Clear white/grey crystals or powder
pH IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION: No data available
BOILING POINT (760mm Hg) 1550oC
MELTING POINT: 457°C
FLASH POINT: Not Applicable
FLAMMABILITY: Not Applicable
EXPLOSIVE PROPERTIES: Not Applicable
SPECIFIC GRAVITY: 5.59
Vapor PRESSURE: Not Applicable
SOLUBILITY IN WATER: 52 x 10-6 g/100g water
SECTION 10. STABILITY: Darkens on exposure to light
HAZARDOUS DECOMPOSITION: May evolve toxic fumes in fire
MATERIALS TO AVOID: Aluminum, Ammonia, Alkali metals, Peroxy compounds, Sulpoxides.STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
SECTION 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
TOXIC DOSE - LD50 >10g/kg oral, mouse
CARCINOGENICITY No evidence of carcinogenic properties.
MUTAGENICITY/TERATOGENICITY No evidence of mutagenic or teratogenic effects.
TOXICOLOGICAL FINDINGS Harmful by ingestion, inhalation and skin contact. Prolonged exposure may result in argyria, a bluish discolouration of the
skin. Irritating to eyes and may irritate skin
SECTION 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
The following applies to silver compounds in general: biological effects: silver ions toxic for aquatic organisms; bacteria: Ps. putida toxic from 0.006 mg/l up; protozoa:
U. parduczi toxic from 0.1 mg/l up; arthropods: D. daphnia LC50: 0.5 mg/l; algae: M. aeruginosa toxic from 0.0007 mg/l up; Sc. quadricauda toxic from 0.009 mg/l up
Due to the poor solubility of the product, no harmful effects on aquatic organisms are to be expected when the product is handled and used with due care and attention.
SECTION 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
DISPOSAL METHODS: Chemical residues are generally classified as special waste, and as such are covered by regulations which vary according to location.
Contact your local waste disposal authority for advice, or pass to a chemical disposal company.
SECTION 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
Not subject to transport regulations
SECTION 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
CLASSIFICATION: Not classified as dangerous according to EC Directives. EC-No.: 232-033-3
LABEL FOR SUPPLY: None
RISK PHRASES: R22 Harmful if swallowed.
SAFETY PHRASES: S24/25 Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
SECTION 16. OTHER INFORMATION
Safety Data Sheet according to Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH). The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any guarantee of the properties of the product. American Elements shall not be held liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale. COPYRIGHT 1997-2022 AMERICAN ELEMENTS. LICENSED GRANTED TO MAKE UNLIMITED PAPER COPIES FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY.

 American Elements manufactures high purity Silver Chloride (AgCl) in both powder and
American Elements manufactures high purity Silver Chloride (AgCl) in both powder and 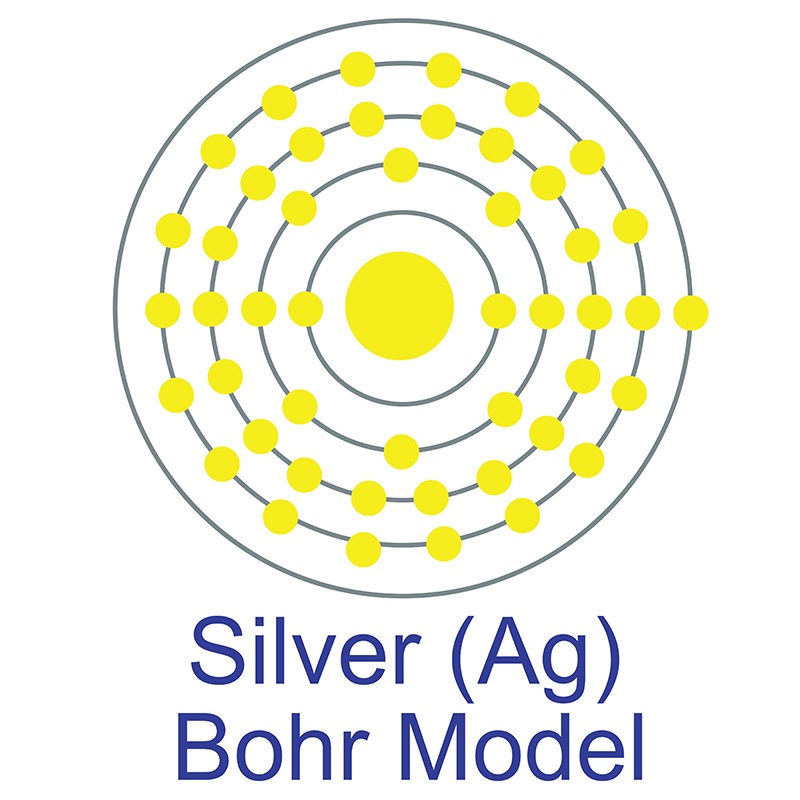 The number of electrons in each of Silver's shells is 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d10 5s1. The silver atom has a radius of 144 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 203 pm. Silver was first discovered by Early Man prior to 5000 BC. In its elemental form, silver has a brilliant white metallic luster.
The number of electrons in each of Silver's shells is 2, 8, 18, 18, 1 and its electron configuration is [Kr]4d10 5s1. The silver atom has a radius of 144 pm and a Van der Waals radius of 203 pm. Silver was first discovered by Early Man prior to 5000 BC. In its elemental form, silver has a brilliant white metallic luster.  It is a little harder than
It is a little harder than 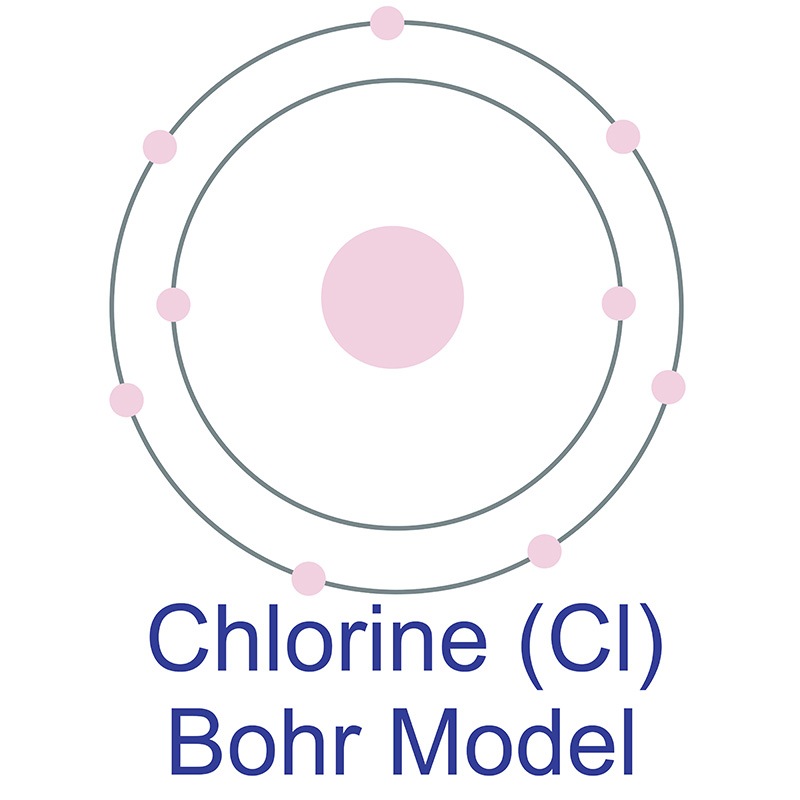 In its elemental form, chlorine is a yellow-green gas. Chlorine is the second lightest halogen after fluorine. It has the third highest electronegativity and the highest electron affinity of all elements, making it a strong oxidizing agent. It is rarely found by itself in nature. Chlorine was discovered and first isolated by Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1774. It was first recognized as an element by Humphry Davy in 1808.
In its elemental form, chlorine is a yellow-green gas. Chlorine is the second lightest halogen after fluorine. It has the third highest electronegativity and the highest electron affinity of all elements, making it a strong oxidizing agent. It is rarely found by itself in nature. Chlorine was discovered and first isolated by Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1774. It was first recognized as an element by Humphry Davy in 1808.