About Selenium
In 1817 the chemists Jons Jakob Berzelius and Johan Gottlieb Gahn decided to investigate a strange red precipitate found by workers at a sulfuric acid plant that they owned together. Initially, the material was believed to be a form of arsenic, which had led workers to discontinue use of the pyrite that had produced it, but the chemists noted that it did not have the expected properties for an arsenic compound. Tellurium was a closer fit, as the powder gave off a smell when burned that was known to be associated with that element, but further investigation showed that the element could not be tellurium either, and the chemists eventually recognized that they had discovered a previously unknown element. Tellurium’s name means “earth,” and Berzelius decided to name the new element for Selene, the moon, because of the similarities between the two.
Selenium is a semiconductor that can take a variety of crystalline structures depending on the conditions under which it is formed. The brick red powder found by Berzelius and Gahn was the form encountered most often as a result of chemical reactions, and when rapidly melted it produces a black vitreous solid often sold industrially, but the most stable form is a dense grey solid. In 1873, Willoughby Smith showed that the electric resistance of grey selenium varies predictably depending on incident light. This property is known as photoconductivity, and tellurium is now known to exhibit it as well, though to a lesser degree. The earliest major uses of selenium were in semiconductor devices such as rectifiers in radio and television tubes, which served to replace the previously used vacuum tubes and which preceded the silicon-based components used today.
Despite the rise of silicon as the major industrial semiconductor, selenium remains relevant to semiconductor technologies. While most selenium rectifiers have been replaced by other technologies, selenium remains in use for surge protection devices in some high-energy DC circuits. As a component of the compound semiconductors copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), indium selenide, gallium selenide, cadmium selenide, and zinc selenide, selenium is essential for production of many thin-film solar cells, and is additionally found in electro-optical devices such as LEDs, lasers, and photoresistors. Notably, recently researchers have shown great interest in the possibilities of using cadmium selenide nanocrystals known as quantum dots in novel solar cells, more efficient LEDs, and in biomedical imaging applications.
Pure amorphous selenium was once a component of every photocopier, where its role as a photoconductor allowed for the production of images based on the areas of light shining through a printed document. Today organic photoconductors have largely replaced selenium in this role, but selenium can also produce images based on exposure to x-rays--images that may be transferred to paper, as in a photocopier, or read directly from charge patterns on the selenium into a computer via a thin film transistor array. This type of x-ray technology never rose to popularity during the age of x-ray films, but has seen renewed interest as digital x-ray imaging systems become the norm. Therefore, amorphous selenium is now is found in many flat-panel digital x-ray machines for medical and dental imaging.
Selenium serves several key functions outside its role as a photoconductive semiconductor. As a component of cadmium sulfoselenide pigments, it can impart a brilliant ruby red hue to materials which incorporate it. In glassmaking, selenium salts are added in small amounts because the red tone cancels out the green tinge lent by iron impurities. Selenium is a component of metal alloys, where it improves machinability of the final material and often replaces the more toxic metal lead.
Though excessive quantities of selenium can be toxic, the element is also an important micronutrient, as it is a necessary cofactor for several enzymes. Because of this key biological role, selenium is sometimes included in nutritional supplements. Notably, the major mechanism of mercury poisoning is the permanent inactivation of these essential enzymes caused by a reaction between mercury and selenium. Therefore the effects of some types of mercury exposure can be partially mitigated by sufficient selenium intake.
Selenium is produced primarily as a byproduct of copper refining, but is also recycled from scrap.
Products
 Selenium exhibits both photovoltaic action, where light is converted directly into electricity, and photoconductive action, where the electrical resistance decreases with increased illumination. Below its melting point, selenium is a p-type semiconductor and has many uses in electronics applications. Selenium is available as metal and compounds with purities from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity). Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Selenium oxide is available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Selenium fluoride is another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Selenium is also available in soluble forms including chlorides. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
Selenium exhibits both photovoltaic action, where light is converted directly into electricity, and photoconductive action, where the electrical resistance decreases with increased illumination. Below its melting point, selenium is a p-type semiconductor and has many uses in electronics applications. Selenium is available as metal and compounds with purities from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity). Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Selenium oxide is available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Selenium fluoride is another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Selenium is also available in soluble forms including chlorides. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
Selenium Properties
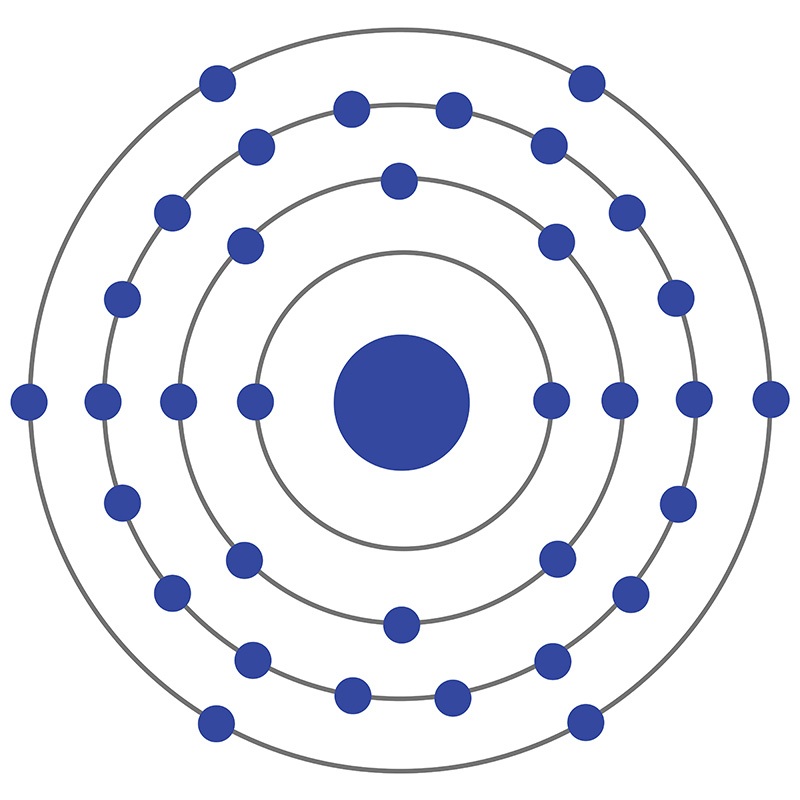
 Selenium is a Block P, Group 16, Period 4 element. The number of electrons in each of Selenium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 6 and its electron configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p4.
Selenium is a Block P, Group 16, Period 4 element. The number of electrons in each of Selenium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 6 and its electron configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p4. 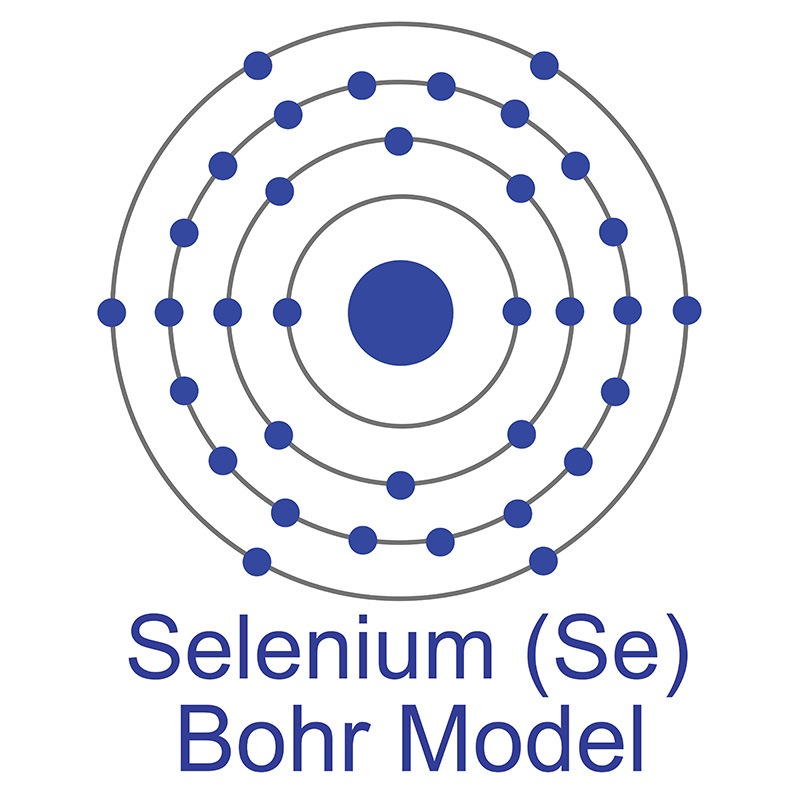 Selenium was discovered and first isolated by Jöns Jakob Berzelius and Johann Gottlieb Gahn in 1817. It is produced from selenide which is found in many sulfide ores. The origin of the name Selenium comes from the Greek word "Selênê" meaning moon.
Selenium was discovered and first isolated by Jöns Jakob Berzelius and Johann Gottlieb Gahn in 1817. It is produced from selenide which is found in many sulfide ores. The origin of the name Selenium comes from the Greek word "Selênê" meaning moon.
Health, Safety & Transportation Information for Selenium
The EPA does not classify selenium as carcinogenic, although selenium sulfide is a probable carcinogen. Selenates and selenites which are compounds of selenium, are highly toxic. Hydrogen selenide gas (SeH2) is the most acutely toxic compound of selenium. Safety data for Selenium and its compounds can vary widely depending on the form. For potential hazard information, toxicity, and road, sea and air transportation limitations, such as DOT Hazard Class, DOT Number, EU Number, NFPA Health rating and RTECS Class, please see the specific material or compound referenced in the Products tab. The below information applies to elemental Selenium.
| Safety Data | |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H331-H373-H413 |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Codes | 23/25-33-53 |
| Safety Precautions | 20/21-28-45-61 |
| RTECS Number | VS7700000 |
| Transport Information | N/A |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling (GHS) |
|
Selenium Isotopes
Selenium (Se) has six naturally occurring isotopes. Five of these are stable: 74Se, 76Se, 77Se, 78Se, and 80Se.
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65Se | 64.96466(64)# | <50 ms | ß+ to 65As; ß+ + p to 64Ge | 3/2-# | N/A | 520.5 | - |
| 66Se | 65.95521(32)# | 33(12) ms | ß+ to 66As | 0+ | N/A | 536.97 | - |
| 67Se | 66.95009(21)# | 133(11) ms | ß+ to 67As; ß+ + p to 66Ge | 5/2-# | N/A | 549.7 | - |
| 68Se | 67.94180(4) | 35.5(7) s | ß+ to 68Br | 0+ | N/A | 566.17 | - |
| 69Se | 68.93956(4) | 27.4(2) s | ß+ to 69As; ß+ + p to 68Ge | (1/2-) | N/A | 576.11 | - |
| 70Se | 69.93339(7) | 41.1(3) min | EC to 70As | 0+ | N/A | 589.78 | - |
| 71Se | 70.93224(3) | 4.74(5) min | EC to 71As | 5/2- | N/A | 598.79 | - |
| 72Se | 71.927112(13) | 8.40(8) d | EC to 72As | 0+ | N/A | 611.53 | - |
| 73Se | 72.926765(11) | 7.15(8) h | EC to 73As | 9/2+ | N/A | 620.54 | - |
| 74Se | 73.9224764(18) | Observationally Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 632.34 | 0.89 |
| 75Se | 74.9225234(18) | 119.779(4) d | EC to 75As | 5/2+ | 0.67 | 640.42 | - |
| 76Se | 75.9192136(18) | STABLE | - | 0+ | N/A | 651.29 | 9.37 |
| 77Se | 76.9199140(18) | STABLE | - | 1/2- | 0.53506 | 659.37 | 7.63 |
| 78Se | 77.9173091(18) | STABLE | - | 0+ | N/A | 669.31 | 23.77 |
| 79Se | 78.9184991(18) | 2.95(38)E+5 y | ß- to 79Br | 7/2+ | -1.018 | 676.46 | - |
| 80Se | 79.9165213(21) | Observationally Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 686.4 | 49.61 |
| 81Se | 80.9179925(22) | 18.45(12) min | ß- to 81Br | 1/2- | N/A | 693.55 | - |
| 82Se | 81.9166994(22) | 97(5)E+18 y | 2ß- to 82Kr | 0+ | N/A | 702.56 | 8.73 |
| 83Se | 82.919118(4) | 22.3(3) min | ß- to 83Br | 9/2+ | N/A | 707.84 | - |
| 84Se | 83.918462(16) | 3.1(1) min | ß- to 84Br | 0+ | N/A | 716.85 | - |
| 85Se | 84.92225(3) | 31.7(9) s | ß- to 85Br | (5/2+)# | N/A | 721.21 | - |
| 86Se | 85.924272(17) | 15.3(9) s | ß- to 86Br | 0+ | N/A | 727.42 | - |
| 87Se | 86.92852(4) | 5.50(12) s | ß- to 87Br; ß- + n to 86Br | (5/2+)# | N/A | 731.77 | - |
| 88Se | 87.93142(5) | 1.53(6) s | ß- to 88Br; ß- + n to 87Br | 0+ | N/A | 737.06 | - |
| 89Se | 88.93645(32)# | 0.41(4) s | ß- to 89Br; ß- + n to 88Br | (5/2+)# | N/A | 740.48 | - |
| 90Se | 89.93996(43)# | 300# ms [>300 ns] | ß- + n to 91Br; ß- to 92Br | 0+ | N/A | 745.76 | - |
| 91Se | 90.94596(54)# | 270(50) ms | ß- to 91Br; ß- + n to 90Br | 1/2+# | N/A | 748.25 | - |
| 92Se | 91.94992(64)# | 100# ms [>300 ns] | ß- to 92Br | 0+ | N/A | 752.6 | - |
| 93Se | 92.95629(86)# | 50# ms [>300 ns] | Unknown | 1/2+# | N/A | 754.16 | - |
| 94Se | 93.96049(86)# | 20# ms [>300 ns] | Unknown | 0+ | N/A | 758.51 | - |