About Cerium
Cerium was discovered in 1803 by Jons Jacob Berzelius and named after the then recently-discovered dwarf planet Ceres. Like most of its fellow rare earth elements--of which it is the most abundant--cerium was initially identified in the form of its oxide, referred to as ceria, and was not obtained as a pure metal until decades after its initial discovery. Nonetheless, both salts and metallic mixtures containing cerium quickly found uses in industry. Cerium salts were found to have anti-emetic properties, and soon found their way into cough tinctures and antibacterial treatments. Around the same time, Carl Auer von Welsbach, an Austrian scientist with a knack for commercializing his discoveries, successfully developed two products requiring the use of cerium: gas mantles and lighter flints. Auer’s gas mantles were simple devices--cotton fabric soaked in mixtures of salts--but the glow they emitted when heated allowed for brighter, whiter light to be shed by gas lamps. Cerium found a third use in the early days of artificial lighting in carbon-arc lamps, which were particularly valued in film studios for their extreme brightness, which allowed them to mimic the look of natural sunlight.
With the exception of cerium nitrate, which is still available as an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory topical treatment for burns, cerium compounds find little use in modern medicine, but the use of cerium in lighting applications has continued and expanded: cerium containing lantern mantles and cerium alloy lighter flints are still in production, but today cerium-containing phosphors are also essential to the production of display screens and fluorescent lamps.
Cerium’s optical properties make it an important component of nontoxic alternatives to cadmium-based pigments and an important additive in the glass manufacturing, where it is used to provide golden coloring and allows for the selective blocking of UV light. Cerium also imparts valuable properties when added in small quantities to various alloys: it makes aluminum more resistant to corrosion, magnesium more resistant to heat, and helps reduce the sulfur and oxygen content of steel. The largest use of cerium by volume is as the polishing agent cerium (IV) oxide, which is used on precision optical components and to polish silicon wafers used in microchips. Cerium oxides are also useful as catalysts, and are used for that purpose in motor vehicle catalytic converters, petroleum refining, and solid oxide fuel cells.
Like other rare earth elements, cerium is never found in its pure form in nature. It can be obtained only from rare earth containing minerals such as xenotime, monazite, and bastnasite, or from ion-adsorption clays.
Products
Cerium is one of the products manufactured and distributed under the tradename AE Rare Earths. Its numerous commercial applications include uses in metallurgy, glass making and glass polishing, ceramics, catalysis, solid oxide fuel cells, and phosphors. In steel manufacturing it is used to remove free oxygen and sulfur by forming stable oxysulfides and by tying up undesirable trace elements, such as lead and antimony. It is considered to be the most efficient glass polishing agent for  precision optical polishing. It is also used to de-colorize glass by keeping iron in its ferrous state. The ability of cerium-doped
precision optical polishing. It is also used to de-colorize glass by keeping iron in its ferrous state. The ability of cerium-doped glass to block out ultra violet light is utilized in the manufacturing of medical glassware and aerospace windows. It is also used to prevent polymers from darkening in sunlight and to suppress discoloration of television glass. Cerium is available as metal and compounds with purities from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity). Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Cerium oxides are available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Cerium fluorides are another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Cerium is also available in soluble forms including chlorides, nitrates and acetates. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
glass to block out ultra violet light is utilized in the manufacturing of medical glassware and aerospace windows. It is also used to prevent polymers from darkening in sunlight and to suppress discoloration of television glass. Cerium is available as metal and compounds with purities from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity). Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Cerium oxides are available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Cerium fluorides are another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Cerium is also available in soluble forms including chlorides, nitrates and acetates. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
Cerium Properties
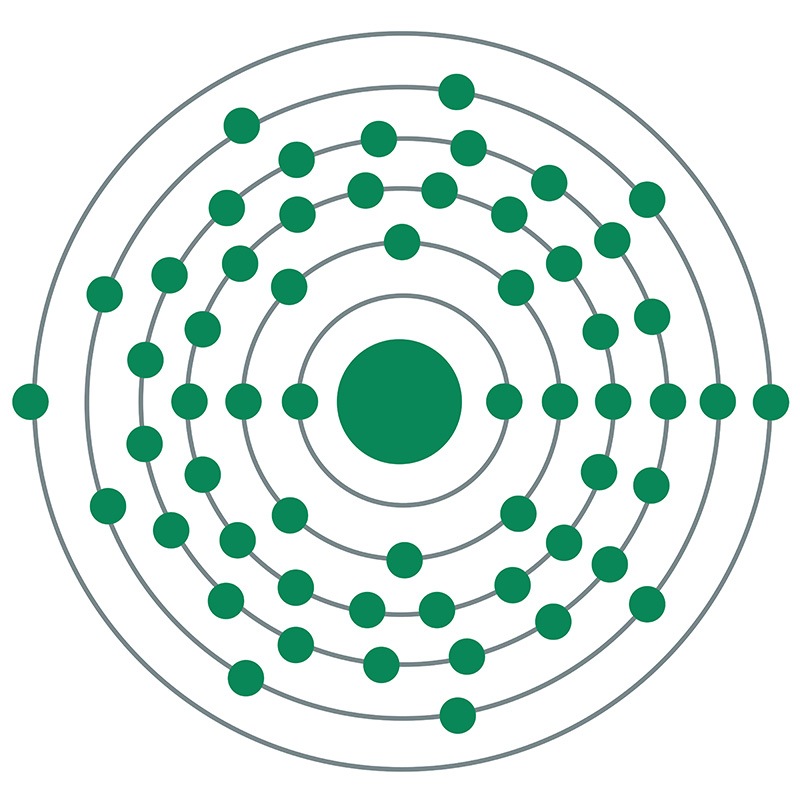
 Cerium is a Block F, Group 3, Period 6 element. The number of electrons in each of cerium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 19, 9, 2 and its electron configuration is [Xe] 4f1 5d1 6s2. The cerium atom has a radius of 182.5.pm and its Van der Waals radius is 235.pm. In its elemental form, CAS 7440-45-1, cerium has a silvery white appearance. Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth metals.
Cerium is a Block F, Group 3, Period 6 element. The number of electrons in each of cerium's shells is 2, 8, 18, 19, 9, 2 and its electron configuration is [Xe] 4f1 5d1 6s2. The cerium atom has a radius of 182.5.pm and its Van der Waals radius is 235.pm. In its elemental form, CAS 7440-45-1, cerium has a silvery white appearance. Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth metals.  . It is, therefore, strongly acidic and moderately toxic. It is also a strong oxidizer. The cerous state closely resembles the other trivalent rare earths.
Cerium is found in the minerals allanite, bastnasite, hydroxylbastnasite, monazite, rhabdophane, synchysite and zircon. Cerium was discovered by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1803. It was first isolated by Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839. The element was named after the asteroid Ceres.
. It is, therefore, strongly acidic and moderately toxic. It is also a strong oxidizer. The cerous state closely resembles the other trivalent rare earths.
Cerium is found in the minerals allanite, bastnasite, hydroxylbastnasite, monazite, rhabdophane, synchysite and zircon. Cerium was discovered by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1803. It was first isolated by Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839. The element was named after the asteroid Ceres.
Health, Safety & Transportation Information for Cerium
Cerium is moderately toxic. Safety data for Cerium and its compounds can vary widely depending on the form. For potential hazard information, toxicity, and road, sea and air transportation limitations, such as DOT Hazard Class, DOT Number, EU Number, NFPA Health rating and RTECS Class, please see the specific material or compound referenced in the Products tab. The below information applies to elemental (metallic) Cerium.
| Safety Data | |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H228-H302-H312-H315-H319-H332-H335 |
| Hazard Codes | F, Xn |
| Risk Codes | 11-20/21/22-36/37/38 |
| Safety Precautions | 16-26-36/37/39 |
| RTECS Number | N/A |
| Transport Information | UN 1333 4.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling (GHS) |
|
Cerium Isotopes
Naturally occurring cerium (Ce) has four stable isotopes: 136Ce, 138Ce, 140Ce, and 142Ce.
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 119Ce | 118.95276(64)# | 200# ms | ß+ to 119La | 5/2+# | N/A | 942.87 | - |
| 120Ce | 119.94664(75)# | 250# ms | ß+ to 120La | 0+ | N/A | 960.26 | - |
| 121Ce | 120.94342(54)# | 1.1(1) s | ß+ to 121La | (5/2)(+#) | N/A | 968.34 | - |
| 122Ce | 121.93791(43)# | 2# s | ß+ to 122La; ß+ + p to 121Ba | 0+ | N/A | 985.74 | - |
| 123Ce | 122.93540(32)# | 3.8(2) s | ß+ to 123La; ß+ + p to 122Ba | (5/2)(+#) | N/A | 993.82 | - |
| 124Ce | 123.93041(32)# | 9.1(12) s | ß+ to 124La | 0+ | N/A | 1001.89 | - |
| 125Ce | 124.92844(21)# | 9.3(3) s | ß+ to 125La; ß+ + p to 124Ba | (7/2-) | N/A | 1019.29 | - |
| 126Ce | 125.92397(3) | 51.0(3) s | ß+ to 126La | 0+ | N/A | 1027.37 | - |
| 127Ce | 126.92273(6) | 29(2) s | ß+ to 127La | 5/2+# | N/A | 1035.45 | - |
| 128Ce | 127.91891(3) | 3.93(2) min | ß+ to 128La | 0+ | N/A | 1052.84 | - |
| 129Ce | 128.91810(3) | 3.5(3) min | ß+ to 129La | (5/2+) | N/A | 1060.92 | - |
| 130Ce | 129.91474(3) | 22.9(5) min | ß+ to 130La | 0+ | N/A | 1069 | - |
| 131Ce | 130.91442(4) | 10.2(3) min | ß+ to 131La | (7/2+) | N/A | 1077.08 | - |
| 132Ce | 131.911460(22) | 3.51(11) h | ß+ to 132La | 0+ | N/A | 1085.16 | - |
| 133Ce | 132.911515(18) | 97(4) min | ß+ to 133La | 1/2+ | N/A | 1093.24 | - |
| 134Ce | 133.908925(22) | 3.16(4) d | EC to 134La | 0+ | N/A | 1110.63 | - |
| 135Ce | 134.909151(12) | 17.7(3) h | EC to 135La | 1/2(+) | N/A | 1118.71 | - |
| 136Ce | 135.907172(14) | Observationally Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 1126.79 | 0.185 |
| 137Ce | 136.907806(14) | 9.0(3) h | EC to 137La | 3/2+ | N/A | 1134.87 | - |
| 138Ce | 137.905991(11) | Observationally Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 1142.95 | 0.251 |
| 139Ce | 138.906653(8) | 137.641(20) d | EC to 139La | 3/2+ | 0.9 | 1151.02 | - |
| 140Ce | 139.9054387(26) | STABLE | - | 0+ | N/A | 1159.1 | 88.45 |
| 141Ce | 140.9082763(26) | 32.508(13) d | ß- to 139La | 7/2- | 1.1 | 1167.18 | - |
| 142Ce | 141.909244(3) | Observationally Stable | - | 0+ | N/A | 1175.26 | 11.114 |
| 143Ce | 142.912386(3) | 33.039(6) h | ß- to 143La | 3/2- | N/A | 1174.02 | - |
| 144Ce | 143.913647(4) | 284.91(5) d | ß- to 144La | 0+ | N/A | 1182.1 | - |
| 145Ce | 144.91723(4) | 3.01(6) min | ß- to 145La | (3/2-) | N/A | 1190.18 | - |
| 146Ce | 145.91876(7) | 13.52(13) min | ß- to 146La | 0+ | N/A | 1198.26 | - |
| 147Ce | 146.92267(3) | 56.4(10) s | ß- to 147La | (5/2-) | N/A | 1197.02 | - |
| 148Ce | 147.92443(3) | 56(1) s | ß- to 148La | 0+ | N/A | 1205.1 | - |
| 149Ce | 148.9284(1) | 5.3(2) s | ß- to 149La | (3/2-)# | N/A | 1213.18 | - |
| 150Ce | 149.93041(5) | 4.0(6) s | ß- to 150La | 0+ | N/A | 1211.94 | - |
| 151Ce | 150.93398(11) | 1.02(6) s | ß- to 151La | 3/2-# | N/A | 1220.02 | - |
| 152Ce | 151.93654(21)# | 1.4(2) s | ß- to 152La | 0+ | N/A | 1228.1 | - |
| 153Ce | 152.94058(43)# | 500# ms [>300 ns] | ß- to 153La | 3/2-# | N/A | 1226.86 | - |
| 154Ce | 153.94342(54)# | 300# ms [>300 ns] | ß- to 154La | 0+ | N/A | 1234.94 | - |
| 155Ce | 154.94804(64)# | 200# ms [>300 ns] | ß- to 155La | 5/2-# | N/A | 1243.02 | - |
| 156Ce | 155.95126(64)# | 150# ms | ß- to 156La | 0+ | N/A | 1241.78 | - |
| 157Ce | 156.95634(75)# | 50# ms | ß- to 157La | 7/2+# | N/A | 1249.86 | - |