About Bismuth
Though bismuth is twice as abundant as gold in the earth’s crust, early man appears to have remained largely ignorant of its existence (with the sole exception of certain bronze Incan knives unearthed in Machu Picchu). The first written reference to the metal was by the German monk Basilius Valentinus in 1450 who called it "wismut," from the German weisse masse (meaning white mass, also translated as meadow mines); around that time, mines in Schönberg began extracting bismuth ores for use in pigments and dyes. 16th century Christian scholar Georgius Agricola was the first to clearly distinguish bismuth as an element distinct from antimony, lead, tin or zinc, metals with which it was frequently misidentified, and Claude François Geoffroy finally isolated the metal in 1738.
The exact etymology of the name bismuth is debated: the most likely candidate is bisemutum, Agricola’s Latinized translation of wismut, but other suggested origins are the Arabic bi ismid, meaning “possessing the properties of antimony,” and psimydos, a corruption of the Greek psimythion meaning “white lead.” Alchemists also referred to the metal as tectum argenti, or "silver being made," due to the frequent presence of bismuth ores atop those of silver. Besides pigments, early uses of bismuth compounds were mainly limited to medical treatments of digestive disorders and as additives to pewter alloys. Demand for bismuth remained low until World War I, when it was utilized in solders and alloys, and rose dramatically throughout the years as it began to be used as an additive in aluminum, iron, and steels, and again when it gained attention as alternative to lead and cadmium due to its low toxicity (unusual for a heavy metal).
Bismuth is classified as a p-block “poor metal,” which refers to its proximity to the border between metals and non-metals on the periodic table. In its elemental form, bismuth is a silvery-white crystalline solid that oxidizes to pink when exposed to air and burns with a blue flame, forming the yellow oxide; high purity bismuth metal can form brilliant rainbow-colored Hopper crystals that are easily grown at home in an oven. Both soft and extremely brittle, bismuth metal is higher in density as a liquid than as a solid, meaning that it expands in volume as it cools; the only other elements that exhibit this property are antimony, germanium, silicon, and gallium. Bismuth has several notable properties: compared to all other metals, it is the most strongly diamagnetic, possesses the lowest thermal conductivity (with the exception of mercury), and exhibits the highest Hall Effect, or increase in electrical resistance in a magnetic field. It is also the heaviest element that is ostensibly stable, its only stable isotope (209-Bi) having a half-life of more than a billion times the age of the universe: 1 yottasecond, the equivalent to 32 quadrillion years. Bismuth occasionally occurs as a free element in nature and in minerals such as bismuthinite, bismite, and bismoclite. It is also produced as a byproduct of lead, copper, tin, molybdenum and tungsten extraction, and by recycling. Its sulfide and oxide forms are the most commercially important.
Applications for bismuth metal and its compounds are numerous. With other metals such as tin, cadmium, and lead, bismuth forms low-melting alloys which are extensively used in the automotive and aviation industries, safety devices in fire extinguishing systems, and solders. Bismuth is also used in malleable irons, steels for free machining, and isostatic lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) used in nuclear reactors; because it expands on solidification, alloys of bismuth are well-suited for the making of sharp castings of objects subject to damage by high temperatures. Bismuth metal is used as a thermocouple material, an electrocatalyst for converting CO2 to CO for alternative fuels, and a carrier for uranium 235-U or 233-U fuel in nuclear reactors. Its soluble salts are characterized by forming insoluble basic salts with the addition of water, a property sometimes used in detection work. Industrial applications for compounds and alloys include solders, lead-free ammunition, additives for casting and galvanizing, lubricants, pyrotechnics, cosmetics, glazes and pigments, and catalysts for making acrylic fibers and high density foams. The most common medical use of bismuth is in the commercial digestive aid bismuth subsalicylate, more commonly known as Pepto-Bismol (57% bismuth by weight).
Crystalline bismuth compounds play an important role in advanced and emerging technologies. Bismuth telluride is a semiconductor that exhibits the thermoelectric effect when alloyed with antimony or selenium. Bismuth selenide is a topological insulator, a unique hybrid material with an insulating core and conductive surface with applications in spintronics-based electronics and quantum computers. Another unique topological insulator is sodium bismuthide (Na3Bi), a type of material known as a “three-dimensional topological Dirac semi-metal” that can be more efficiently fabricated than its two-dimensional analog of graphene. Researchers have identified superconducting bismuth compounds like silver-doped bismuth oxysulphide and bismuth strontium calcium copper oxide (BSCCO), one of several materials that exhibits the highest measured superconducting transition temperatures. Bismuth Ferrite (BFO) is a perovskite crystal that is piezoelectric, multiferroic, and can act as a nanoscale shape memory material for integrating photonic and electrical components in plasmonic devices or used in high-temperature supercapacitors for electric vehicles.
Products
 Bismuth expands on solidification. This property makes bismuth alloys particularly well suited to the making of sharp castings of objects subject to damage by high temperatures. With other metals such as tin, cadmium, etc., bismuth forms low-melting alloys which are extensively used for safety devices in fire detection and extinguishing systems. Bismuth is also used in producing malleable irons and is finding use as a catalyst for making acrylic fibers.
Bismuth expands on solidification. This property makes bismuth alloys particularly well suited to the making of sharp castings of objects subject to damage by high temperatures. With other metals such as tin, cadmium, etc., bismuth forms low-melting alloys which are extensively used for safety devices in fire detection and extinguishing systems. Bismuth is also used in producing malleable irons and is finding use as a catalyst for making acrylic fibers.  When bismuth is heated in air it burns with a blue flame, forming yellow fumes of the oxide. The metal is also used as a thermocoupling material, and has found application as a carrier for 235 U or 233 U fuel in nuclear reactors. Its soluble salts are characterized by forming insoluble basic salts with the addition of water, a property sometimes used in detection work. Bismuth oxychloride is used extensively in cosmetics. Elemental or metallic forms of bismuth include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Bismuth oxide is available in forms including powders and dense pellets for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Bismuth fluorides are another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Bismuth is also available in soluble forms including chlorides, nitrates and acetates. These compounds are manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
When bismuth is heated in air it burns with a blue flame, forming yellow fumes of the oxide. The metal is also used as a thermocoupling material, and has found application as a carrier for 235 U or 233 U fuel in nuclear reactors. Its soluble salts are characterized by forming insoluble basic salts with the addition of water, a property sometimes used in detection work. Bismuth oxychloride is used extensively in cosmetics. Elemental or metallic forms of bismuth include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Bismuth oxide is available in forms including powders and dense pellets for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Bismuth fluorides are another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Bismuth is also available in soluble forms including chlorides, nitrates and acetates. These compounds are manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
Bismuth Properties
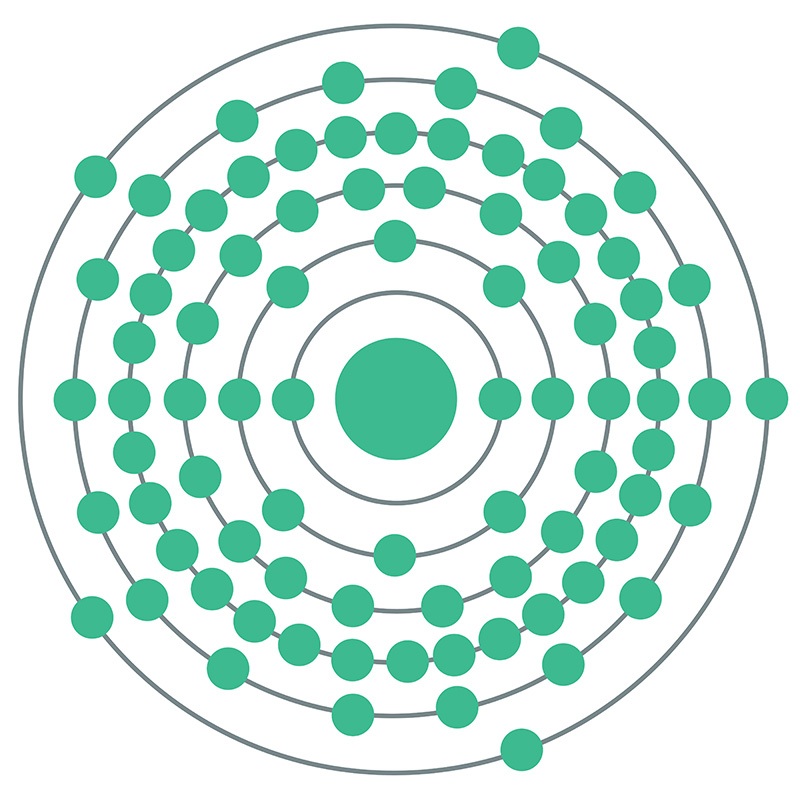
 Bismuth is a Block P, Group 15, Period 6 element. The number of electrons in each of Bismuth's shells is 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 5 and its electron configuration is [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p3.
Bismuth is a Block P, Group 15, Period 6 element. The number of electrons in each of Bismuth's shells is 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 5 and its electron configuration is [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p3.  The bismuth atom has a radius of 154.5.pm and its Van der Waals radius is 200.pm. In its elemental form, CAS 7440-69-9, bismuth is a silvery white brittle metal. Bismuth is the most diamagnetic of all metals and, with the exception of mercury; its thermal conductivity is lower than any other metal.
The bismuth atom has a radius of 154.5.pm and its Van der Waals radius is 200.pm. In its elemental form, CAS 7440-69-9, bismuth is a silvery white brittle metal. Bismuth is the most diamagnetic of all metals and, with the exception of mercury; its thermal conductivity is lower than any other metal. Bismuth has a high electrical resistance, and has the highest Hall Effect of any metal (i.e., greatest increase in electrical resistance when placed in a magnetic field). Bismuth is found in bismuthinite Bi2S3 and bismite Bi2O3. It is also produced as a byproduct of lead, copper, tin, molybdenum and tungsten extraction. The name Bismuth originates from the German word 'wissmuth' meaning white mass. Bismuth information, including technical data, safety data, high purity properties, research, applications and other useful facts are discussed below. Scientific facts such as the atomic structure, ionization energy, abundance on earth, conductivity and thermal properties are also included.
Bismuth has a high electrical resistance, and has the highest Hall Effect of any metal (i.e., greatest increase in electrical resistance when placed in a magnetic field). Bismuth is found in bismuthinite Bi2S3 and bismite Bi2O3. It is also produced as a byproduct of lead, copper, tin, molybdenum and tungsten extraction. The name Bismuth originates from the German word 'wissmuth' meaning white mass. Bismuth information, including technical data, safety data, high purity properties, research, applications and other useful facts are discussed below. Scientific facts such as the atomic structure, ionization energy, abundance on earth, conductivity and thermal properties are also included.
Health, Safety & Transportation Information for Elemental Bismuth
Bismuth is not toxic, however, safety data for Bismuth metal, nanoparticles and compounds can vary widely depending on the form. For potential hazard information, toxicity, and road, sea and air transportation limitations, such as DOT Hazard Class, DOT Number, EU Number, NFPA Health rating and RTECS Class, please see the specific Bismuth material or compound referenced in the “Products” tab. The below information applies to elemental (metallic) Bismuth.
| Safety Data | |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H228 |
| Hazard Codes | F |
| Risk Codes | 11 |
| Safety Precautions | 16 |
| RTECS Number | EB2600000 |
| Transport Information | UN 3089 4.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | nwg |
| Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling (GHS) |
|
Bismuth Isotopes
Bismuth (Bi) has no stable isotopes. While Bismuth-209 has traditionally been considered a stable isotope, it is now known that it has a half-life of over 1.9×1019 years.
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 184Bi | 184.00112(14)# | 6.6(15) ms | Unknown | 3+# | N/A | 1393.35 | - |
| 185Bi | 184.99763(6)# | 2# ms | p to 184Pb | 9/2-# | N/A | 1410.75 | - |
| 186Bi | 185.99660(8) | 14.8(7) ms | a to 182Tl; ß+ to 186Pb | (3+) | N/A | 1418.82 | - |
| 187Bi | 186.993158(16) | 32(3) ms | a to 183Tl; ß+ to 187Pb | 9/2-# | N/A | 1426.9 | - |
| 188Bi | 187.99227(5) | 44(3) ms | a to 184Tl; ß+ to 188Pb | 3+# | N/A | 1434.98 | - |
| 189Bi | 188.98920(6) | 674(11) ms | a to 185Tl; ß+ to 189Pb | (9/2-) | N/A | 1452.38 | - |
| 190Bi | 189.9883(2) | 6.3(1) s | a to 186Tl; ß+ to 190Pb | (3+) | N/A | 1460.46 | - |
| 191Bi | 190.985786(8) | 12.3(3) s | a to 187Tl; ß+ to 191Pb | (9/2-) | N/A | 1468.53 | - |
| 192Bi | 191.98546(4) | 34.6(9) s | ß+ to 192Pb; a to 188Tl | (3+) | N/A | 1476.61 | - |
| 193Bi | 192.98296(1) | 67(3) s | ß+ to 193Pb; a to 189Tl | (9/2-) | N/A | 1484.69 | - |
| 194Bi | 193.98283(5) | 95(3) s | ß+ to 194Pb; a to 190Tl | (3+) | N/A | 1492.77 | - |
| 195Bi | 194.980651(6) | 183(4) s | ß+ to 195Pb; a to 191Tl | (9/2-) | N/A | 1500.85 | - |
| 196Bi | 195.980667(26) | 5.1(2) min | ß+ to 196Pb; a to 192Tl | (3+) | N/A | 1508.93 | - |
| 197Bi | 196.978864(9) | 9.33(50) min | ß+ to 197Pb; a to 193Tl | (9/2-) | N/A | 1526.32 | - |
| 198Bi | 197.97921(3) | 10.3(3) min | ß+ to 198Pb | (2+,3+) | N/A | 1534.4 | - |
| 199Bi | 198.977672(13) | 27(1) min | ß+ to 199Pb | 9/2- | N/A | 1542.48 | - |
| 200Bi | 199.978132(26) | 36.4(5) min | ß+ to 200Pb | 7+ | N/A | 1550.56 | - |
| 201Bi | 200.977009(16) | 108(3) min | ß+ to 201Pb; a to 197Tl | 9/2- | N/A | 1558.64 | - |
| 202Bi | 201.977742(22) | 1.72(5) h | ß+ to 202Pb; a to 198Tl | 5(+#) | N/A | 1566.72 | - |
| 203Bi | 202.976876(23) | 11.76(5) h | ß+ to 203Pb; a to 199Tl | 9/2- | N/A | 1574.8 | - |
| 204Bi | 203.977813(28) | 11.22(10) h | ß+ to 204Pb | 6+ | N/A | 1582.87 | - |
| 205Bi | 204.977389(8) | 15.31(4) d | EC to 205Pb | 9/2- | 4.16 | 1590.95 | - |
| 206Bi | 205.978499(8) | 6.243(3) d | EC to 206Pb | 6(+) | 4.6 | 1599.03 | - |
| 207Bi | 206.9784707(26) | 32.9(14) y | EC to 207Pb | 9/2- | 4.08 | 1607.11 | - |
| 208Bi | 207.9797422(25) | 3.68(4)E+5 y | EC to 208Pb | (5)+ | N/A | 1615.19 | - |
| 209Bi | 208.9803987(16) | 1.9(2)E+19 y | a to 205Tl | 9/2- | 4.1106 | 1613.95 | 100 |
| 210Bi | 209.9841204(16) | 5.012(5) d | ß- to 210Po; a to 206Tl | 1- | -0.0445 | 1622.03 | - |
| 211Bi | 210.987269(6) | 2.14(2) min | a to 207Tl; ß- to 211Po | 9/2- | N/A | 1630.11 | - |
| 212Bi | 211.9912857(21) | 60.55(6) min | ß- to 212Po; a to 208Tl; ß- + a to 208Pb; | 1(-) | N/A | 1628.87 | - |
| 213Bi | 212.994385(5) | 45.59(6) min | a to 207Tl; ß- to 211Po | 9/2- | N/A | 1636.95 | - |
| 214Bi | 213.998712(12) | 19.9(4) min | ß- to 214Po; a to 210Tl; ß- + a to 210Pb; | 1- | N/A | 1645.03 | - |
| 215Bi | 215.001770(16) | 7.6(2) min | ß- to 215Po | (9/2-) | N/A | 1643.79 | - |
| 216Bi | 216.006306(12) | 2.17(5) min | ß- to 216Po | 1-# | N/A | 1651.87 | - |
| 217Bi | 217.00947(21)# | 98.5(8) s | Unknown | 9/2-# | N/A | 1659.95 | - |
| 218Bi | 218.01432(39)# | 33(1) s | Unknown | 1-# | N/A | 1658.71 | - |